Introduction
I. Scope
II. Design
III. Organization
IV. collection
V. Disaggregation
VI. Review
VII. Publication
VIII. Assessment
IX. Management
Introduction:
The General Authority for Statistics (GaStat) applies in all its statistical work a unified methodology that conforms with the nature of each statistical product. It depends on the Handbook of Statistical Work Procedures, which is compatible with internationally approved procedures. Statistical products go through eight major stages, in addition to a ninth stage represented in the
comprehensive “management”stage which is illustrated in the following figure and the subsequent explanations:
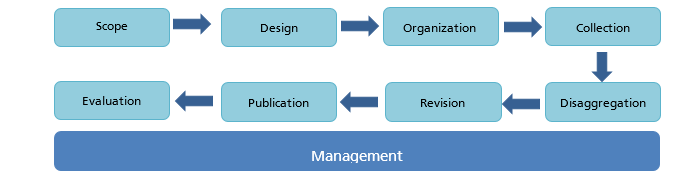
The first three stages (scope, design and organization) are collaborative stages between GaStat and its clients who are data users from development entities. The fourth stage (data collection) is a collaborative stage between GaStat and the statistical population, whether they are households or establishments, to take data and information. The remaining stages (disaggregation,
reviewing and publication) are statistical and are undertaken by GaStat. Afterwards, the eighth stage (assessment) is again done in collaboration with the clients. The management stage is administrative and organizational and spans all other stages. Those stages have been applied to the internal trade survey as follows:
First Stage: Scope:
It is the starting point for producing the internal trade survey. It is also the first collaborative stage between GaStat and a number of parties that benefit from the survey results, mainly the Ministry of Economy and Planning, the Ministry of Commerce and Investment, the Council of Chambers of Commerce, the Small and Medium Enterprises Authority, the Job Creation Commission and the Ministry of Labor and Social Development). Workshops and meetings were held at this stage between GaStat and those parties to better understand their needs and know their requirements, given that they are the main beneficiaries of the internal trade survey results.
The views of those parties are taken into consideration to ensure the attainment of all the goals of the internal trade survey which are summed up as follows:
• To know the volume of internal trade activity (wholesale and retail trade and vehicle sale, repair and maintenance).
• To identify the volume of the internal trade activity contribution to domestic product.
• To provide statistics on the activities of wholesale and retail trade and vehicle sale, repair and maintenance to develop short-term indicators that help in identifying the growth rates of internal trade activity.
• To know the volume of seasonal variation in the number of employees and the volume of compensations, expenses and revenues (sales).
• To provide recent statistics that help decision makers reduce unemployment and increase the contribution of creating jobs in the private sector within the internal trade activity.
• To provide the requirements of government bodies and departments and researchers in terms of statistical data and information on the internal trade activity.
• To meet the requirements necessary for compiling national accounts in line with the latest international systems.
• To use those data for the purposes of local, regional and international comparisons and conducting studies and analyses.
Second Stage: Design:
This stage is for designing statistical work as an integrated product. It also includes identifying the statistical population, designing the statistical framework and the survey sample along with its questionnaire, identifying the method and tools of data collection and identifying the sampling units. Clients are made partners in all those procedures to benefit from their observations to meet all requirements and ensure that they are part of the statistical product.
The most important outputs of this stage are:
1. The Statistical Population:
The target statistical population within the internal trade survey bulletin is composed of all establishments working in the activities of vehicle sale and repair and wholesale and retail trade which are included in the Classification of Economic Activities (ISIC4) in the Kingdom.
2. Statistical Sources:
The internal trade survey bulletin uses in its data the field survey of establishments (internal trade survey) which is done by GaStat quarterly and is listed under the classification of economical statistics. Data is collected in the survey through visiting a sample of establishments that work in the activities of vehicle sale and repair and wholesale and retail trade and represent all administrative regions of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, as well as completing an electronic questionnaire that includes a number of questions. Estimation and indicators are provided within the survey in relation to the internal trade survey.
3. Internal Trade Survey Terminology and Concepts:
3.1. Internal Trade: It is a quarterly survey that includes the activity of wholesale and retail trade and is considered a survey on commercial establishments engaged in the activity of wholesale or retail selling any type of commodities without carrying out any conversion of the commodity. It also includes repairing motor vehicles and motorcycles.
3.2. Establishment: It is an economic business unit with a legal entity which has a fixed location, where a certain economic activity is carried out, and is owned by a person, a group of persons, a company, a semi-governmental sector or an enterprise. It is the smallest economic unit which can have data on employees and their compensations, in addition to data on expenses, revenues (sales) and variations in fixed assets.
3.3. Economic Activity: It involves all business or services that are done or provided by an establishment and get it a return. The establishment sometimes does not receive a return on its business as in the case of charities which depend on donations.
3.4. Employees: They are all (Saudi and non-Saudi) individuals who already do paid or unpaid work for the establishment as well as the owners of the establishment or their relatives or workers, be they full-timers or part-timers, permanent or temporary workers or male or female workers, regardless of the fact that their wages are paid on a daily, weekly or monthly basis. The definition also includes partners and members of joint stock companies, in addition to heads and members of the boards of directors. It also includes employees who are entitled to paid leave.
3.5. Compensation of Employees: It is the total periodic payable amounts paid by the establishment to the employees in return for regular working hours and the fixed bonuses given to them, i.e. salaries or wages, in addition to perquisites and allowances which represent payments in cash or in kind offered by the employer to the employees except for wages and salaries. Those payments include all types of bonuses and perquisites, such as education grants and tuition payments for the employees or those who they support, in addition to payments for food or accommodation and payments for social security, transport allowance and overtime pay.
3.6. Operating Expenses: It means the value of all commodities or services already used by the establishment during the fiscal year as a result of conducting their business, whether those requirements were bought in the same year or supplied from stock bought in past years.
3.7. Operating Revenues (Sales): It includes the sales of goods purchased for the purpose of selling them in the same condition as the value of purchase for such goods was recorded, whether the sales are for the main activity (wholesale or retail trade) or were for the secondary activity (wholesale or retail trade). It also includes cash revenues earned when the establishment is engaged in the activity of maintenance and repair of motor vehicles or other secondary activities.
3.8. Variations in Fixed Assets: It involves the identification of fixed assets (stock) and the variations in them in the form of purchased additions or exclusions.
3.9. Online Sales: It involves all sales made when the establishment has e-sales, whether the e-sale is directly made by the establishment or by a business agent.
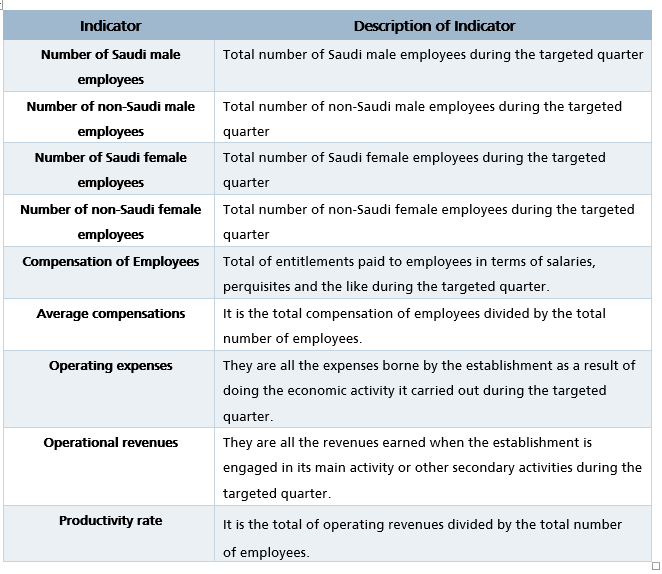
4. Indicators
The following are the main indicators of the internal trade survey:
5. Adopted Statistical Classification:
Classification is defined as being an arranged set of related categories used for data collection according to similarity. It is the basis for collecting and publishing data in all statistical fields, such as economic activity, products, expenditures, jobs or health, etc. It allows for classifying data and information through putting them into meaningful categories to produce useful statistics, considering that data collection requires precise and methodological arrangement in accordance with their common features so that the statistics can be reliable and comparable. The internal trade survey is subject to international standards in terms of collecting and classifying its data as it uses the National Classification of Economic Activities.
5.1 National Classification of Economic Activities (ISIC REV.4):
It is a statistical classification that adopts the International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities (ISIC) which is the reference classification of productive activities. The purpose of using such classification in the internal trade survey is to specify the main economic activity undertaken by the establishment.
Economic activity is defined as being all business or services that are done or provided by an establishment and get it a return. The establishment sometimes does not receive a return on its business as in the case of charities which depend on donations.
Designing Survey Questionnaire:
Field Data Collection Questionnaire: The survey questionnaire was prepared and designed by business statistics specialists at GaStat in accordance with international recommendations and standards. It was also presented to internal trade specialists and experts during their visit to GaStat and to the concerned parties to get their observations and remarks about it. The question
wording was prepared in a specific scientific method with the aim of unifying the manner in which researchers direct questions.
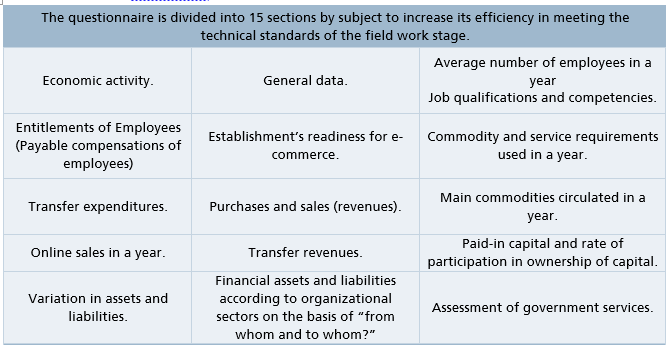
The complete questionnaire can be read and downloaded via GaStat’s official website.
After being approved, the survey questionnaire will be transformed into an electronic questionnaire that can be handled through the advanced data collection system using tablet devices. The system has the following features:
1. Reviewing the work zone of the field researcher (survey sample).
2. Reaching the sample (establishment) using the map on the tablet device.
3. Completing the data with high quality using data auditing and navigation rules to automatically detect input errors and illogical inputs when the data are completed.
Communicating with supervising entities by exchanging remarks with the field researcher.
6. Coverage:
6.1 Spatial Coverage:
The internal trade survey covers the thirteen administrative regions of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The survey covered the regions of Riyadh, Makkah, Madinah, Qassim, Eastern Province, Asir, Tabuk, Hail, Northern Borders, Jazan, Najran, Al-Baha and Al-Jouf. Greater importance was given to cities on the grounds that they contain around 84% of total establishments in the Kingdom and have nearly 91% of total employees in the Kingdom through visiting a sample of establishments in each region that are chosen in a scientific way, so that the sample would represent all economic establishments in the region.
6.2 Temporal Coverage:
It is carried out during the period set for visiting the targeted establishments of the survey sample and completing the survey questionnaire data. The survey data are usually associated with the quarter that precedes the period of conducting it.
6.3 Statistical Framework:
• The 2010 Establishment Census was used as list containing all community items.
• The list, maps and analytical standards of the units were set to choose data providers (establishments).
• The required descriptive data were identified in order to establish the statistical framework and the test framework and also to verify it and use it for the current survey round.
6.4 Sample Design:
6.4.1. A perfect plan is designed and documented to choose the sample units from which data will be collected with providing guarantee for obtaining efficient and highly effective estimations. Therefore, the survey community was divided into non-overlapping parts characterized by the homogeneity of their units. Every part is considered a layer, and every layer is treated as being an independent community where a random sample would be drawn separately from every layer. At the end, all drawn sampling units will be integrated to form an aggregate sample.
6.4.2. Choosing the sample units is done on the basis of the 2010 Establishment Census. In order to choose samples for surveys and statistical studies targeting establishments in general, the framework was divided into four categories on the basis of the establishment size as follows:
• Micro-establishments: It includes all establishments that have a workforce of 1-5.
• Small establishments: It includes all establishments that have a workforce of 6-49.
• Medium establishments: It includes all establishments that have a workforce of 50-249.
• Large establishments: It includes all establishments that have a workforce of more than 250.
6.4.3. Perfect methodology is prepared to choose the sample units with the aim of providing high-quality outputs with minimum burden on data providers using methods of rotation and overlap control.
6.4.4. Required descriptive data are specified to apply the statistical framework and to allocate and choose the sample.
6.4.5. The sample is tested, assessed and verified, and its use in the current frequency of the project is approved.

Third Stage: Organization:
It is the final preparation stage and precedes the visits to establishments and data collection. In this stage, the required workflow procedures are established for preparing the internal trade survey, starting with the collection stage and ending with the assessment stage and the organization and grouping of such procedures. The optimal sequence of those procedures is chosen to arrive at a methodology that achieves the goals of the internal trade survey. Those procedures were also described and documented to facilitate any updates to them in future rounds. The statistical workflow procedures were tested and examined to ensure their compliance with the requirements of preparing the internal trade survey in their final form, approve the procedures of the statistical workflow, and put a road map for implementation.
Testing the efficiency of input systems and the process of transmitting, synchronizing and reviewing data through the tablet system or the office system of the internal trade survey are the main procedures in this stage.
Fourth Stage: Collection:
First: The survey sample was chosen through identifying 11130 establishments as a selected sample that represents the survey community at the level of the Kingdom and is distributed among the thirteen administrative regions of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Second: The workers, who were nominated as field researchers and would later visit establishments to collect the internal trade survey data, were chosen on the basis of several practical and subjective criteria related to the nature of work, such as:
• Educational level.
• Fieldwork experience.
• Personal attributes, such as good conduct, evidence of senses and physical and psychological fitness.
• Nominee’s success in the training program of the internal trade survey.
• The nominee shall not be under the age of 20.
Third: All nominees (GaStat staff and collaborators from some government entities) were qualified and trained through special training programs as follows:
• A training program was held for competent staff members in GaStat headquarters for one week.
• Similar training programs were held for collaborating inspectors, observers and researchers from all the regions of the Kingdom.

Fourth: The method of direct contact with the establishment was adopted in the process of completing the survey questionnaire and data collection. The field researchers visited the establishments located within the survey sample after arriving at it using the coordinates recorded on the tablets and the guiding maps and introducing themselves and showing official documents proving
their statistical identity. They also clarified the aim of their visit. They also presented an overview of the survey and its objectives and took permission to complete the establishment data directly using the electronic questionnaire of the internal trade survey.
They completed the electronic questionnaire through verbal discussions with the owner of the establishment or any official in the establishment with knowledge of its affairs.
Fifth: All field researchers used tablet devices to collect the survey questionnaire data according to timeframes specified for navigating the survey sections and the questionnaire items.
Sixth: Field researchers at all work locations in the Kingdom used the “synchronization” feature available on the tablets devices to download and transfer the completed data of the establishments directly to the database linked to them at GaStat’s headquarters where they are stored in a specific way to be reviewed and processed at a later stage.
Seventh: Check rules are applied electronically to guarantee the consistency, precision and rationality of the data of the internal trade survey questionnaire. They are electronic rules that identify contradictions between answers and were built through linking the logical relationship between the answers to the questionnaire and its variables to help field researchers directly identify any errors upon completing the survey data with the owner of the establishment. Those programmed rules don’t allow any mistakes to go through when an answer contradicts with another piece of information or another answer in the questionnaire.
Eighth: The collected data were verified by being reviewed by the field researcher himself or his inspector and the survey supervisor in the supervision area. All work areas were subjected to a process of monitoring and reviewing from the data quality room at GaStat’s headquarters. The room also controls and monitors the performance of all working groups in the field in synchronization with the time of performing the data collection process starting from the first day to the last.
Data Quality Room:

Fifth Stage: Disaggregation:
The processes of disaggregating the raw data of the internal trade survey used the inputs of classification and coding formed during the data collection process, as they were disaggregated according to the National Classification of Economic Activities (ISIC REV.4) or any other classification or coding like the geographic data classification (such as data distribution at the level of administrative regions). The internal trade survey data were also displayed in suitable tables so that they can be easily summed up, understood and comprehended to obtain results from them, compare them with other data and extract statistical indications from them about the study community. It will also be easy to refer to them in the form of tables without the need to read the original questionnaires which often include some data, such as the names and addresses of establishments and the names of data providers in violation of the principle of statistical data confidentiality.
Data is processed at this stage through taking a number of steps, mainly:
First: Verifying data comprehensiveness and rationality:
Data was reviewed to ensure its comprehensiveness, rationality and accuracy in a way that suits the nature of such data as a prelude to processing data, extracting results and carrying out the final reviewing in the stages that follow the disaggregation stage with the aim of adding quality and accuracy to the provided statistics.
Second: Data anonymization:
To ensure data confidentiality, GaStat removed identifiers from a set of input field survey data, such as hiding the name and address of the establishment owner and other identifiers to ensure the protection of people’s privacy.
Sixth Stage: Reviewing
First: Verifying data outputs:
After reviewing the accumulated data of the internal trade survey and verifying them, GaStat conducted at this stage processes of calculating and extracting results and uploaded and stored them on the database. The final reviewing processes were conducted by specialists in business statistics using modern technologies and software designed for the purposes of reviewing and checking.
Second: Handling of confidential data:
Pursuant to Royal Decree No.23 dated 07/12/1397, GaStat is committed to the absolute confidentiality of all completed data and not using them except for statistical purposes. Therefore, data are safely stored on GaStat’ss servers.

Seventh Stage: Publication:
First: Preparing and setting designed data for publication:
In this stage, GaStat uploaded data results from the internal trade survey database. Afterwards, publication tables and graphs for data and indicators were prepared, had descriptive and methodological data added to them and were prepared in Arabic and English.
Second: Preparing media material and announcing the date of releasing the bulletin:
After GaStat’s announcement about the date of releasing the bulletin on its official website at the beginning of the calendar year, the authority prepares the media material of the announcement of issuing the bulletin on all media outlets as well as its various social media platforms. The announcement will be made on the date set for publication. The bulletin will be published on the official website in various templates of open data in Excel format
to guarantee its circulation and accessibility to all clients and parties interested in internal trade. The bulletin will be included in the website’s statistics library.
Third: Communicating with the clients and providing them with the bulletin:
GaStat pays great importance to communicating with the clients who use the data. Therefore, GaStat communicates with the clients upon the publication of the internal trade bulletin to provide them with it. GaStat also receives the clients’ questions and enquiries about the bulletin and its results through all communication channels so that clients can communicate with the authority to request data. Questions and inquiries are received via:
• GASTAT official website www.stats.gov.sa
• GASTAT official e-mail info@stats.gov.sa
• Client support’s email cs@stats.gov.sa
• Visiting GASTAT head office in Riyadh or in one of its branches in Saudi Arabia
• Official letters
• Statistical helpline (920020081)
Fourth: Preserving the published content:
GaStat’s Documents and Archives Center stored and archived the data of the bulletin to refer to it at any time on request. GaStat took that step out of its awareness of the importance of electronically preserving those data to easily refer to them when needed.
Eighth Stage: Assessment:
After the results are released and received by GaStat’s clients, the clients are contacted again in this stage which allows for assessing the whole statistical process that was carried out, with the aim of constant improvement to obtain high-quality data. The improvements may include methodologies, processes, systems, statistical researchers’ skill and statistical frameworks. This stage is done in collaboration with data users and GaStat’s clients through a number of steps:
First: Collecting measurable assessment inputs:
Main comments and remarks are collected and documented from their sources at all stages, including those collected and documented during the collection stage, such as comments and remarks presented by data collectors and their field supervisors, in addition to data collected and documented during the assessment stage such as the remarks deduced by specialists concerned with reviewing, checking and analyzing data collected from the field. Finally, comments and remarks presented by data users are collected and documented after publication, in addition to what is being monitored via media outlets or the clients’ remarks which GaStat receives through its main channels.
Second: Making the assessment:
Collected assessment inputs are analyzed, and on that basis a number of improvements and possible solutions are defined and discussed with concerned parties in all competent departments in the authority or its clients who are partners in the internal trade bulletin. This step also involves performance measurement of the clients’ use of the results of the internal trade bulletin and their satisfaction with them, contacting unsatisfied clients and providing clarifications to them.
On the basis of those procedures, an agreement will be made on the suggested recommendations to obtain high-quality data in the following round.
Ninth Stage: Management:
This stage is comprehensive as it spans every stages of producing the internal trade survey bulletin. It involves drawing up the general production plan which includes feasibility study, risk management, means of funding and spending mechanisms, as well as developing performance indicators, quality parameters, human resources map necessary for production, following up on the execution of tasks assigned to all departments in every stage, and making reports to ensure that the authority fulfills its commitments towards its clients.
Allah is the Arbiter of Success.
عنوان الملف:
Wholesale and Retail trade Statistics
