Introduction
1. First: Scope
2. Second: Design
3. Third: Organization
4. Fourth: Data collection
5. Fifth: Data disaggrregation
6. Sixsth: Revision
7. Seventh: Publication
8. Eighth: Evaluation
9. Ninth: Management
Introduction:
In all its statistical work, GASTAT applies a unified methodology suitable for the nature of each statistical product using the Statistical Procedures Guide approved by international organizations. Statistical products undergo 8 main stages, in addition to a ninth comprehensive stage ”Management”, as shown in the following diagram and explanation underneath :
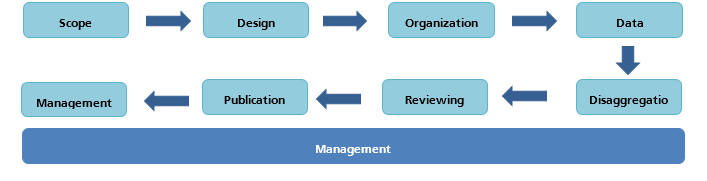
The first 3 stages (Scope, Design and Organization) are cooperative processes between GASTAT and its clients, represented by developmental entities data users, while stage 4 (Data Collection) is done through GASTAT’s cooperation with the statistical population, whether households or establishments, in order to complete data and information. The remaining stages are statistical stages in which data is classified, reviewed and published. Then, stage 8 (Evaluation) is carried out with clients. However, the Management stage is an administrative and organizational procedure applied across all stages. These stages have been applied to Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey as follows:
First stage: The scope:
The starting point of the preparation of the (Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey) and the first shared stage between GASTAT and other partners from relevant entities, represented in The Ministry of Communication and Information Technology and The Communications and Information Technology Commission. At this stage, a number of meetings and workshops were held between GASTAT and those entities to understand their needs and requirements, their feedback were also considered to ensure the realization of all the objectives of the survey, which can be summarized as:
1) This survey aims at providing updated data and indicators about the individuals and households ‘ICT access and usage in a way that helps decision and policy makers to identify the following:
• The rate of information and communications technology devices availability by households. .
• Households ‘ICT access
• The rate of using information and communications technology by individuals.
• Age groups who use ICT
• Educational status of individuals who use ICT
• Occupational status of individuals who use ICT
• Recognizing the fields in which information and communications technology is utilized by individuals.
• Identifying the reasons of not being able to access information and communications technology.
• The places where individuals use information and communications technology
• Difficulties that individuals face while using information and communications technology
• Identifying the reasons of not utilizing information and communications technology.
• The rate of households ‘postal services use
2) It also aims to found a wide database to be used as a reliable reference when conducting studies and research in the field of individuals and households ‘information and communication technology.
Moreover, it has been confirmed that the published statistics would contribute in fulfilling the requirements of Saudi Vision 2030. In addition to other international requirements represented in measuring the sustainable development goals SDGs.
Second stage: The design:
During this stage, a complete design for the statistical product in addition to the tools and methods of data collection, statistical community, survey form, and sampling units are all set forth. Clients are engaged in all these processes to take their feedback into account, so that the product would live up to their expectations.
The most important outcomes of this stage are:
1. Statistical population:
The targeted statistical population of the Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey is composed of all individuals (Saudis and non-Saudis) who live habitually in Saudi Arabia.
2. Statistics source:
Data of the survey is based on the field survey of Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage that GASTAT conducts in a yearly basis. This survey is listed under the classification of (knowledge statistics), where data is collected through visiting a sample of households from the 2010 census. Those households represent all administrative regions of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Data is also collected by completing an electronic questionnaire that includes a number of questions.
3. Terminologies and concepts related to the Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey:
7.1. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) :
A description of the tools and methods of IT access. It also refers to being able to recall, save, organize, and process data. Moreover, it describes the means of information display and exchange through manual and electronic methods. Some of the IT tools are: computers, scanners, digital cameras, telephones, faxes, CDs, and software such as the database system, and multimedia applications.
7.2. ICT Access and Usage:
It is important to differentiate between what we mean by accessing ICT and using ICT. ICT access refers to the availability of such technology to the household .
On the other hand, ICT usage refers to the actual usage of ICT by one or more members of the household either inside the dwelling units or elsewhere.
7.3. Television:
Television is a device that receives TV broadcast signals using common access means such as over the air, central cable, or satellites. The television is usually a separate set or integrated with other devices such as computer or cell phone .
7.4. Radio:
It is a device that receives radio signals using general frequencies such as: LW, AM, FM, SW. The radio can be a separate device or integrated with another device such as an alarm clock, Walkman, cell phone, or a computer.
7.5. Computer:
The computer includes a desktop computer, laptop, or a tablet. It does not include devices that are equipped with integrated computerized tools such as smart televisions or smart phones.
7.6. Desktop computer:
A computer that is fixed to one place. User sits usually in front of the computer and uses the keyboard.
7.7. Laptop:
A portable small sized computer that performs the same tasks as the desktop computer. It includes small computers such as "Notebook", but does not include tablet computers and other similar hand-held computers.
7.8. Tablet:
A computer integrated in the touch flat screen. The user touches the screen instead of using the regular keyboard.
7.9. Cell phone:
It uses a cellular technology that permits access to the public switched telephone network ( PSTN). It includes digital and cellular symmetry technology such as Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) 2000 of the 3rd generation, and 4th generation, and Advanced Mobile Systems Subscribers are of two types: Prepaid or postpaid (bill) subscribers.
7.10. Smart cell phone:
A phone that enables the user to surf the Internet, check e-mail, open office files, and it contains a complete keyboard. It is also defined as the phone that uses one of the following operation systems: Windows phone, Symbian and its affiliated programs, Lennox and its affiliated programs, and BlackBerry. Smart phones do not differ from laptops or personal computers. All smart devices are composed of two integrated parts: hardware (the physical part), and Software (the programming operation system
7.11. Regular cell phone:
A phone that provides the user with the service of making or receiving phone calls, and sending SMS or media messages.
7.12. Internet:
The Internet is a public and international computer web that provides access to communications services including world web. It transfers e-mails, news, entertainment, and data files disregarding the device used. Access is not restricted to computer solely, as it is available also via cell phone, tablet, PDA, games tools, and digital television, etc. Access is possible through fixed or mobile communication network.
7.13. Digital subscriber line (DSL):
A technology that connects high broadband to dwelling units and small economic establishments via regular copper phone lines.
7.14. USB, Portable Modem:
The device that transmit digital signals issued from a computer or a digital device or another to symmetric signal of a telephone line, and it removes the formation of the received symmetric signal and transform it into a digital signal to the digital device.
7.15. Mobile Phone Packages:
Different products with different components (duration of the phone call, number of messages, internet flow…) and different prices. They are provided by various telecommunication companies in a certain country or region .
7.16. Optical Fibers:
Flexible tiny optical wires that carry data in the form of light. This technology is characterized with extreme speed and it allows making use of utmost speed on the line with a speed larger 60 times than that of DSL.
7.17. Mobile Network:
A communication network in which the last connection is a wireless one. The network is distributed on land areas called cells, each one operates at least one transmitter or receiver. This network usually has three sites or transceivers stations. These stations provide the cell with a network coverage that can be used to send data, sounds, and others. The cell usually uses different sets of frequencies from the surrounding cells in order to prevent overlapping and provide high-quality service inside each cell .
7.18. Wireless Network Wi –Fi:
Wi-Fi network is the brief form of Wireless Fidelity. This network can be accessed by using radio waves without wires. An example of Wi-Fi usage is joining an internet network in any place without using wires.
7.19. Wired Network:
Networks are classified according to the way of connection. It is called a wired one when the devices are connected with each other via braided copper cables, optical fibers, and other connecting cables
7.20. Broadband:
A general term that refers to a signal or a communication device that uses a wider broadband in comparison with a regular signal or normal device. The movement capacity is higher when the broadband is wider. In data communications this term refers to the rate of transferring data which is not less than 256 Kbit/s.
7.21. Kbit/s (Kbit/s or kbps):
Kilobyte per secon (one kilobyte/second is 1000 bytes/second) A data unit = 1024 bytes. One byte represents 1 or 0 in Binary Digit system, or "true" or "false" in Logic system.
7.22. Megabyte MB:
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Its recommended unit symbol is MB. The unit prefix mega is a multiplier of 1000000 (106) in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one megabyte is one million bytes of information.
It is widely used to refer to the data transmission rates in computer networks or communication systems. The network transmission rate and download speed usually use MB as a transmission unit.
7.23. Fixed Telephone Line:
It refers to the telephone line that connects the user device ( a telephone or a fax) to the public switched telephone network PSTN, which has a specific port on the telephone exchange.
7.24. E-Waste:
E-waste is a popular, informal name for electronic products nearing the end of their "useful life." Fixed phone, Mobile phone, Computer, laptop, tablet and television).
7.25. Storage:
When the household does not need or use any device or equipment but it still keeps it in its dwelling .
7.26. Waste Container:
The container used for home wastes disposal. These wastes are collected by companies/institutions responsible for wastes collection.
7.27. Recycling:
The recycling of E-wastes to produce new material that can be used in other fields.
7.28. Given or granted to other:
When the household does not need any device or equipment, it gives it to others ( individuals who do not belong to the household)
7.29. Mail Box:
Mailbox is a metallic box that is hanged on the wall outside of the establishment for the purpose of exchanging messages. It is also known as: An address dedicated for an individual or a given agency, and it is placed in a place called (post office). The owner or owners of the mailbox have the right to use it in sending and receiving messages, envelops, and parcel posts in return of paying a specific sum of money in case of renting the mailbox. The rent of the mailbox in such case shall be in accordance with the provisions indicated by the country to which the post office is affiliated.
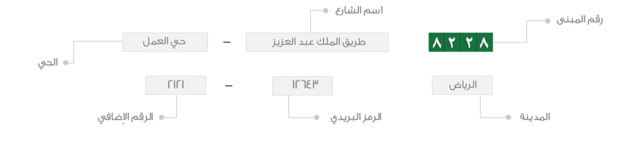
7.30. National Address:
It is a unified national address all over KSA. The address is created by Saudi Post in accordance with standard technological specifications to facilitate identifying sites. This is accomplished through establishing a modern addressing communication system that represents the base for e-government applications and e-commerce activities. The address consists of three main parts: Postal Code, Building No., additional No as clarified in the following figure:
7.31. Social Media:
Websites aiming to connect a group of individuals or establishments worldwide. Some of the social media services are: ability to chat with others in writing, verbal communication, and visual communication. Some of ) Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat, ...etc) these networks are
7.32. E-mail:
It is a tool that enables network local and international users to exchange messages, texts, and attachments from one computer to another inside or outside the establishment.
7.33. Blog:
Blog is a discussion site or an advertisements site on the world wide web and consists of posts ordered chronologically from the recent to the older.
7.34. Government E-services:
A system adopted by governmental entities by using internet to connect their devices with each other. It is also used to link the entity services with other establishments and the public in general. By using these services, individuals and establishments can access any information easily, in a way that would create a transparent, quick, and accurate relationship for a high quality performance.
4. Indicators:

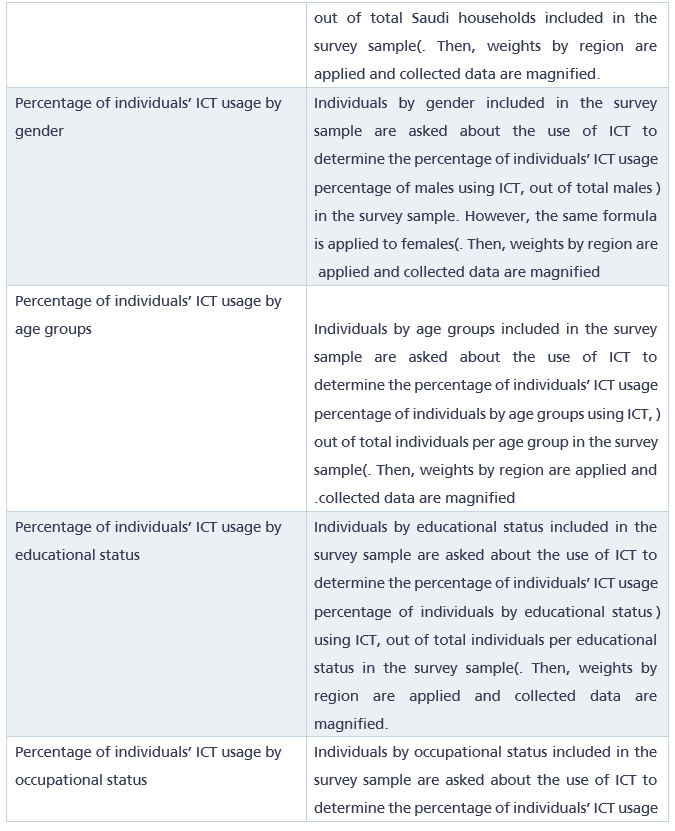
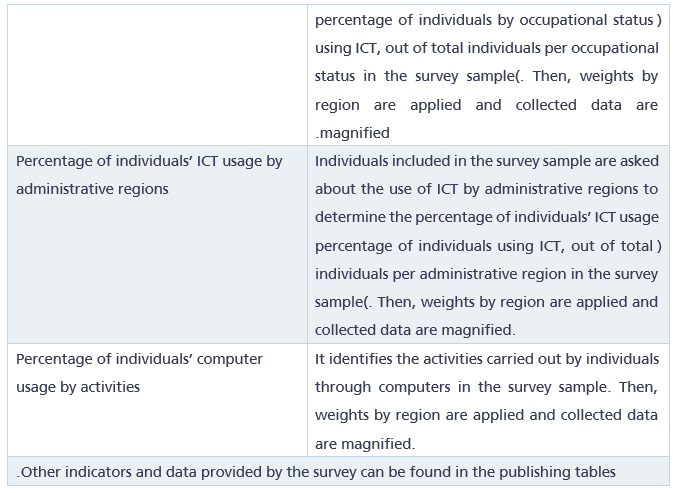
5. Used statistical classifications:
Classification is defined as being an arranged set of related categories used for data collection according to similarity. It is the basis for collecting and publishing data in all statistical fields, such as economic activity, products, expenditures, jobs or health, etc. It allows for classifying data and information through putting them into meaningful categories to produce useful statistics, considering that data collection requires precise and methodological arrangement in accordance with their common features so that the statistics can be reliable and comparable. The Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage survey is subject to international standards in terms of collecting and classifying its data as it uses the following classification:
First: Saudi Occupation Classification:
Is an approved statistical classification based on the International Standard Occupation Classification (ISCO) that provides a policy of classifying and collecting occupational information that are obtained by statistical census and surveys as well as administrative records. The purpose of using such classification in the labour force survey is to classify workers according to their occupations.
Second: National Guide of Countries and Nationalities:
Is a comprehensive, unified, standardized and international classification for countries and their affiliated territories. It is based on the international standard Country Code (ISO 3166); the classification provides codes for countries and their affiliated territories. Using such codes and numbers instead of the name of the country is very useful for statistical purposes where it saves time and avoid any errors. In order to classify Saudi and non-Saudi individuals, this classification was applied.
6. Design of survey questionnaire:
• Field data questionnaire: the survey questionnaire was designed and prepared by specialists of Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey at the General Authority for Statistics. International recommendations, standards, and definitions have been taken into consideration. The questionnaire has been also reviewed by specialists and experts in the field of individuals and households ICT access and usage. It has been also reviewed by related entities to take their comments and feedbacks. The questions have been written in a scientific way to be asked in a unified way by researchers.
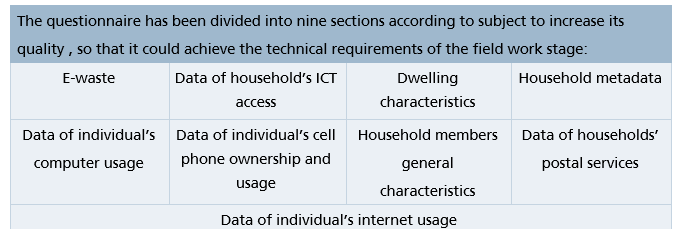
The full version of the questionnaire can be viewed and downloaded via:
After being approved, the questionnaire has been transferred into an electronic version to be used on the developed data collection system by using tablets devices, which have the following features:
1- Ability to allocate the field researcher work area (survey sample).
2- Ability to reach the sample (the household) by using maps on tablets.
3- Completing data with high quality by using data auditing and transfer rules (to automatically discover the entry errors and non-logical inputs once data are completed).
4- Facilitating communication between supervising categories by sending and receiving comments and notes to and from researchers.
7. Coverage:
7.1. Spatial coverage:
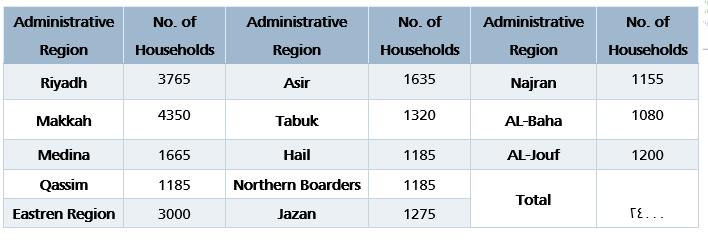
The Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey covers data related to households in all 13 administrative regions of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, which are: Riyadh, Makkah, Madinah, Qassim, Eastern Region, Asir, Tabuk, Hail, Northern Borders, Jazan, Najran, Al-Baha, and Al-Jouf. . A scientifically selected sample is visited in each region representing households of that region.
7.2. Temporal coverage:
The metadata of the household, the housing characteristics, and data of household ICT access are referred to the time during which the household was visited.
The household members’ characteristics such as marital, educational, and occupational status are referred to the week preceding the household visit.
Data of E-waste and postal services are referred to the last (12) preceding the household visit.
Data of individuals use of cell phone, computer, and internet are referred to the last (3) months preceding the household visit.
8. Statistical framework
The General Framework of the Households Census 1431 H (2010) which was updated in (2018) is used
The units’ analytical characteristics, lists and maps are developed to select data providers (households).
Metadata are determined to create a statistical and a test framework that is validated to be used during the current round of the survey.
9. Sample design:
9.1. A perfect plan is designed and documented to choose the sample units from which data will be collected with providing guarantee for obtaining efficient and highly effective estimations. Therefore, the survey community was divided into non-overlapping parts characterized by the homogeneity of their units. Every part is considered a layer, and every layer is treated as being an independent community where a random sample would be drawn separately from every layer. At the end, all drawn sampling units will be integrated to form an aggregate sample.
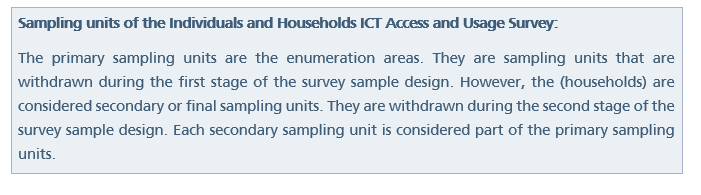
9.2. Choosing the sampling units from the statistical frameworks that have been designed to cover the targeted statistical community. The sample selection process is done through two stages: in the first stage, the primary sampling units are selected, which are the enumeration areas from the framework of buildings and real-estate units coding system. (1200) enumeration areas are selected within the census frame. These areas are distributed on all classes in all the administrative regions by using the suitable method to the size, considering the number of Saudi households in them. Then, the final sampling units (households) are randomly drawn from the enumeration areas chosen in the first stage using a regular random sampling method with (20) households in each enumeration area, which means a total of (24000) households all over Saudi Arabia.
9.3. Perfect methodology is prepared to choose the sample units with the aim of providing high-quality outputs with minimum burden on data providers using methods of rotation and overlap control.
• Required metadata are specified to apply the statistical framework and to allocate and choose the sample.
• Sample has been selected, evaluated, validated, and used in the current frequency of the project.
Third stage: Organization
It is the last stage of preparation stages that precedes the process of household visit and data collection. The work procedures required for the preparation of the Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey have been prepared in this stage. They will begin from the next stage "collection stage" and will end with the “Evaluation stage”. In addition, the procedures are organized and collected and their appropriate order is determined in order to reach a methodology that achieves the objectives of the Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey. These procedures were also described and documented to facilitate the updates in the future cycles. Furthermore, the statistical work procedures were tested to ensure that they meet the requirements of the preparation of the Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey in its final form. Then, the procedures of the statistical work are approved, and the road map of the implementation is developed.
Testing the efficiency of input systems and the process of transmission, synchronization and review of data, which is carried out through tablets or desktops of the Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey, is one of the most important procedures at this stage.
Fourth stage: Data collection
First: survey’s sample was selected by identifying 24,000 households to represent the survey’s community at Saudi Arabia’s level, which are distributed as follows:
Second: selection of candidates as field researchers to visit households for (Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey) data collection was based on a number of criteria that are related to the nature of work, such as:
Educational level
Experience in field works
Personal qualities, such as: good behavior and physically and mentally fit
Candidate must pass the training program of Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey
Candidate’s age must not be less than 20 years’ old
Third: all candidates were well trained (GASTAT’s staff as well as co-operators from some governmental entities) and that was through special training programs, as follows:
Conduct a training program for the specialized staff at GASTAT’s headquarter for one week.
Conduct similar training programs for the co-operators of inspectors, monitors and researchers in various regions of Saudi Aribia.

Fourth: Direct contact with the household in the process of completing the survey questionnaire and data collection: Each field researcher visited the households within the sample of the survey after reaching them using the coordinates in the tablet and the guide maps. He also identified himself and presented the official documents proving his statistical identity. In addition, he explained the purpose of his visit and provided an overview of the survey and its objectives. Then, the researcher completed the household’s data by filling an an electronic questinnaire.
Fifth: All field researchers used tablets to complete survey questionnaire data based on the time reference specified according to the number of household members and their demographic, social and economic characteristics.
Sixth: Field researchers in different regions of the Saudi Arabia used the "synchronization" feature available on tablets to upload and transfer the household data directly to the database associated with it at the headquarters of GASTAT, where it is stored in a specific format for review and subsequent processing.
Seventh: (Auditing rules) are applied to ensure the consistency, accuracy and logic of the data on the Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey questionnaire. This is done through an (electronic bases that detect the discrepancy of answers). These bases were built by linking the logical relationship between the answers of the questionnaire and its variables to help the field researcher to detect any error directly when completing data with the household. These bases will not allow the passing of errors if the answer conflicts with another information or answer in the questionnaire.
Eighth: The data collected was verified by reviewing the data through the same field researcher, his inspector and the supervisor on the survey in the supervision area. All the work areas were subjected to a process of monitoring and reviewing from the data quality room at the headquarters of GASTAT. This room also monitors and controls the performance of all working groups in the field in synchronization with the time of the data collection process implementation from the first day to the last day.
l

Fifth stage: Disaggregation
During this stage, raw data of the Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage are disaggregated based on the classification and coding inputs completed during the data collection process. They were disaggregated based on ISIC,Rev, 4 and the National Classification of Countries and Nationalities or any other classification or coding such as the distribution of data at the level of administrative regions, and the qualitative and descriptive classification such as individual’s gender and marital status. Furthermore, data of Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey are presented in right tables in order to summarize, understand, as well as extract their results. Moreover, to compare them with other data, and to obtain statistical significances about the selected community. However, referring to such data indicated in tables is much easier than going back to check the original forms that may include some data like names and addresses of household heads and data providers, which might violate the confidentiality of the statistical data.
During this stage, specialists of Knowledge statistics Department have processed and analyzed data through a number of steps:
• Sorting and arranging data in sequence or in different groups or categories.
• Summarizing detailed data into key points or data.
• Combining many data segments and make them interconnected.
• Processing missing data.
• Processing illogical data.
• Converting data into statistically significant data.
• Organizing, presenting, and interpreting data.
One of the most important data processing procedures carried out is “data anonymization”. To ensure data confidentiality, GASTAT removes identifiers from the input fields for the survey data, such as hiding the name and address of the establishment owner and other identifiers to protect people’s privacy.
Sixth stage: Revision
First: Data Outputs Validation:
In addition to the revision process applied to the collected data of Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey in the fourth stage to check their accuracy, all the outputs are stored and uploaded to the database after being calculated by GASTAT to be reviewed and processed by specialists of Knowledge Statistics through modern technologies and software designed for this purpose.
Second: Dealing with confidential data:
According to the Royal Decree No. 23 dated 07-12-1397, data must always be kept confidential, and must be used by GASTAT only for statistical purposes. Therefore, the data are protected in the data servers of the Authority.

Seventh stage: Publication
First: Preparation and Process of the Results Designed for Publishing:
During this stage, GASTAT downloaded the data results from the database of Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage surveys. Then, publishing tables and charts of data and indicators, metadata, and methodology were all prepared and processed to be published in both languages English and Arabic.
Second: Preparing Media Kit and Announcing the Date of the Release:
The publication date of the bulletin is already set up by GASTAT on its official website at the beginning of the Calendar Year. During this period, the Authority is preparing the media kits to announce the date of releasing the bulletin through media, in addition to its various platforms in social networking sites. The bulletin will be published firstly on GASTAT’s official website in different formats, such as Excel format to be easily reached for all clients and those who are interested ICT access and usage in general. It will be uploaded on the website’s statistics library as well.
Third: Communicate with the clients and provide the bulletin to them:
GASTAT believed in the importance of communication with the clients, therefore, once the bulletin is released, GASTAT will communicate with the clients and provide them with the bulletin. GASTAT will receive the questions and enquiries about the bulletin and its results through its various channels. Requests and enquiries are received through:
- GASTAT official website www.stats.gov.sa
- GASTAT official e-mail info@stats.gov.sa
- Client support’s email cs@stats.gov.sa
- Visiting GASTAT head office in Riyadh or in one of its branches in Saudi Arabia.
- • Official letters
- Statistical help line (920020081)
Fourth: Preservation of published content:
The Bulletin’s data are preserved and archived by the documents and archives center at the Authority to be used as a reference at any time. GASTAT carried out this step to preserve such data electronically to be used again when needed.
Eighth stage: Evaluation
All GASTAT’s clients who used the results of the Bulletin will be contacted again in order to assess the entire statistical process. This is done for improvement purposes in order to obtain high-quality data. The improvements include: methodologies, procedures and systems, statisticians’ skill level, as well as statistical work frameworks. This stage is carried out with data users and GASTAT clients according to the following steps:
First: Collecting measurable assessment inputs:
The most important comments and notes are collected and documented from their sources in different stages, for example comments and notes given by data collectors and their field supervisors. Also, notes written by specialists responsible for reviewing, auditing, and analyzing data collected from the field team or administrative regions. Finally, comments and notes collected and documented by data users after publishing the Bulletin, or social media comments and clients’ feedback that sent to the Authority through its main channels.
Second: the Evaluation procedure:
It is done by analyzing the collected assessment inputs, and comparing the results of this analysis with the ones predicted previously. Therefore, a number of possible improvements and solutions are identified and discussed with specialists, experts, and concerned partners. During this step, clients' performances and satisfaction levels of using the results of Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey are measured. Based on these procedures, the recommendations for obtaining high quality data for the next statistics are all agreed upon.
Ninth stage: Management
It is a comprehensive stage that is required to carry out each stage of the Individuals and Households ICT Access and Usage Survey production. During this stage, the plan was set, which includes the feasibility study, risk management, financing methods, in addition to expenditure mechanisms. The plan also covered the development of performance indicators, quality criteria, and manpower map required for production. Through this plan, the implementation process of the tasks assigned to different departments at each stage will be followed up and reported to ensure that GASTAT meets its clients’ requirements.
عنوان الملف:
Metadata Report of ICT Access and Use by Households and Individuals Survey 2022
نوع الصفحة:
بيانات الوصفية
