Introduction
The Labor Market Statistics Publication is one of the important statistical products issued by the General Authority for Statistics (GASTAT). It is a quarterly publication that collects its data from two sources; First source: the survey (the Labor Force Survey), and the second source: the data of administrative records of the authorities concerned with the labor market (the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development, the General Organization for Social Insurance, and the National Information Center). This publication, in addition to the rest of the statistical products issued by the authority, contributes to support decision and policy makers, and it includes: statistics of employees and job seekers based on many basic variables according to the administrative distribution of the Kingdom’s regions such as: nationality, gender, age groups, and educational level, in addition to the main indicators extracted from the labor force survey estimates such as unemployment rates, labor force participation, employment, and others indicators.
The Labor Market Statistics Publication is an extension of the Labor Force Survey report, which began to be issued annually in 1999 and continued as an annual publication until 2007, then turned into a semi-annual publication and became a quarterly publication starting from the second quarter of 2016. In the fourth quarter of 2016, it was developed to be a publication that collects the survey results with the administrative records of the authorities concerned with the labor market in the Kingdom under the name (Labor Market Statistics Publication).
The importance of these publications stems from the fact that it provides comprehensive statistics on the labor market in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and contributes to building a statistical database for the labor market that can be used in preparing and planning future, social, and economic development programs in the Kingdom.
The General Authority for Statistics extends its thanks and appreciation to all partners and clients from the authorities concerned with the labor market in the Kingdom for their cooperation in the completion of the labor market statistics publication. It also extends its thanks to the heads of households for their response to enumerators and answering the labor force survey questionnaire, as their cooperation had the greatest impact in completing the data collection processes in the survey.
The General Authority for Statistics is pleased to receive your suggestions and comments about this publication via (info@stats.gov.sa) to improve its content and add further development to future publications.
The General Authority for Statistics
Methodology
GASTAT implements all its statistical works in accordance with a unified methodology that complies with the nature of each statistical product. It relies on the Manual of the Statistical Procedures which conforms with the procedures adopted by the international statistical organizations. The statistical product goes through eight inter-connected stages, in addition to a ninth stage (the comprehensive "management" stage), which are as follows:
The first three stages: (Scope, design, and organization) are collaborative stages between GASTAT and its partners from the different developmental entities. However, the fourth stage (Data collection) is a collaborative stage between GASTAT and the statistical community either households or establishments, to complete data and information. On the other hand, the rest of the stages are considered statistical stages carried out by GASTAT, including (Tabulation, revision, and publication). After that, the eighth stage (Evaluation) is done through collaboration with clients again, whereas the (Management) stage is an administrative and organizational stage that relates to all stages. These stages have been applied on the labor market statistics as follows:
1. First stage: Scope
The is the first step in the process of producing Labor Market Statistics, and it is also the first collaborative stage between GASTAT and the labor market group which includes the Ministry of Human resources and Social Development, General Organization of Social Insurances, and Human Resources Development Fund, in addition to the National Information Center, private sector, and the academic sector. Many workshops and meeting have been held between GASTAT and these organizations to understand their needs and requirements as they are considered data providers and users at the same time.
The feedback of these organizations has been taken into consideration to assure the achievement of all “Labor Market Statistics” objectives which can be summarized as follows:
- Supporting decision makers and policy makers, researchers, and those who are interested in getting up-to-date and comprehensive statistics related to the labor market in Saudi Arabia.
- Empowering public and private sectors to investigate the labor market changes and make use of them.
- Providing the academic sectors with the requirements of social and economic studies and research.
- Providing up-to-date statistics on:
- Unemployment rate according to many variables.
- Unemployed individuals and labor force according to many variables.
- Employment according to many variables.
- Labor Force Participation rate and employment to working age population rate.
- Average wages and average working hours.
- Job seeking method, period of unemployment, and previous work and training experiences.
In this stage, we ensure that all published statistics contribute to meeting the requirements of Saudi Vision 2030. They also must cover the regional requirements such as the requirements of GCC-STAT, and other international requirements such as the International Labor Organization (ILO).
2. Second stage: Design
The stage of designing the statistical work as it is considered a whole product. Through this stage, the statistical community is determined, statistical framework, survey sample, and questionnaire are designed, methods and tools of data collection are identified, and sampling units are specified. Partners collaborate in all these procedures to benefit from their feedbacks, so that all requirements can be achieved within the statistical product.
The most important outputs of this stage are:
2.1Statistical community
Statistical community of labor market statistics consists of all individuals (Saudis and non-Saudis) who habitually live in Saudi Arabia.
2.2Statistics sources
Labor market statistics data are based on two main sources to provide comprehensive information on the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia labor market conditions. They include statistics from the Labor Force Survey (household survey) which GASTAT conducts quarterly. They also include quarterly data from administrative records of related governmental entities. GASTAT currently releases indicators form these two data sources separately, so that data from each source can be released as soon as it is ready.
2.2.1First source of labor market statistics: Labor Force Survey
It is a multiple mode household survey conducted by GASTAT under the social statistics category. Information is collected by contacting a sample of households from all administrative regions of Saudi Arabia and completing an electronic questionnaire that includes several questions asked about household members. The survey is conducted in both CATI and CAPI mode. This survey provides estimates and indicators of labor force characteristics of all persons 15 years and above who live in Saudi Arabia, including key indicators of labor market such as the unemployment rate and the labor force participation rate and the employment-to-population ratio.
2.2.2Second source of labor market statistics: Administrative records
These data are recorded and updated data and information of governmental entities that are related to labor market. They result from the official electronic registration and documentation operations of these entities. Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development, General Organization of Social Insurance, and the National Information Center periodically provide GASTAT with their recorded data through the electronic linkage, as these entities are considered key references of workers data in both the public and private sectors in Saudi Arabia.
The following table shows the type of data provided by each entity from the labor market statistics sources:
|
2.3Terminologies and concepts of labor market statistics
2.3.1Terminologies and concepts of the Labor Force Survey
(First source of Labor Market statistics)
2.3.1.1Survey statistical framework
In Q4 2022, a sample redesign was introduced as part of a broader transformation of the LFS. The frame for the redesigned sample is the list of dwellings created from the 2022 Census of Housing and Population. The telephone number and ID number of the head of household of all occupied residential dwellings were obtained during the 2022 Census of Population and Housing. The LFS frame consists of all residential dwellings at the time of the 2022 Census, whether occupied, vacant or under construction. This frame is used for selection of the LFS sample from Q4 2022 onwards.
2.3.1.2Sample of Dwellings
A sample of dwellings was chosen from the frame. The sample was drawn from all dwellings, regardless of their status as occupied, vacant or under construction at the time of the 2022 Census of Population and Housing. Details of the sampling methodology is presented in section 2.11.
The choice of the dwelling as the sampling unit introduced in the previous redesign that was implemented in Q4 2021 has been maintained. This was a change of sampling unit from Household to Dwelling that was made during the previous redesign because dwelling represents a more stable unit for sampling purposes.
2.3.1.3Administrative Region
It is a part of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, and its administration is supervised by a government agency directly affiliated with the Ministry of Interior, such as the Riyadh region and the Makkah region, etc. In each administrative region there is a city that is the seat of its emirate. There are 13 Administrative Regions in the Kingdom.
2.3.1.4Governorate
It is part of the administrative region and is considered the first administrative level within its components and is affiliated to it administratively, such as Al-Kharj Governorate, which is affiliated to the Riyadh region.
2.3.1.5Center
It is the administrative authority affiliated to the governorate, such as Al-Hayathim Center affiliated to Al-Kharj Governorate, and some of them follow the headquarters of the Emirate directly, such as the Irqah Center directly affiliated to the Emirate of Riyadh Region.
2.3.1.6Population name
It is every place that has a fixed population such as a city, a village, or a farm, or a non-fixed one, such as a water resource.
2.3.1.7City
According to the population census, every population name that has a municipality or whose population exceeds (5000) people is considered a city.
2.3.1.8Neighborhood
It is a part of the city that includes a set of national addresses, streets, and roads. It has a well-known name and is often surrounded by main streets that separate it from other neighborhoods. The neighborhoods have been given numbers at the city level starting with the number (001) and ending with the number of the last neighborhood in the city. The divisions of neighborhoods have been approved According to the divisions followed by the secretariats and municipalities.
2.3.1.9Village
According to the population census, a village is a place that has a fixed population, has a recognized name, and has a population of less than 5,000 people.
2.3.1.10National address
It is a system that was developed by the Saudi Postal Corporation (Sobol), relying entirely on geographic information systems, through which a special number was created for each piece of land (building or vacant land), and it was linked to spatial coordinates, and this number is used to access each piece easily through various technical map applications.
2.3.1.11Building
It is every self-contained structure that is fixed to the ground permanently or temporarily and consists of one or more rooms and has an entrance or several entrances that lead to all its contents. The building may be for economic, social or religious activity such as house, villa, mosque, tent, school , hospital.
Noting that the building’s appurtenances, such as the garage, the shop, and the villa’s appendage, are not considered separate buildings, just as the buildings of bridges, electric rooms, engine rooms, and water pumps are not considered unless any of these sites are used for housing at the time of enumeration. Also, buildings under construction are not considered within the buildings. Unless bases, foundations and walls are erected.
2.3.1.12Real Estate Unit
It is a building or part of a building that has a separate door, whether it is intended for housing or work, housing and work, or a public housing, and it may be vacant or under construction.
2.3.1.13Dwelling
It is a building or part of a building originally intended for the residence of one or more households and has a separate door whether at the time of the visit it is occupied by one or more households or vacant, and it may contain one or more establishments, and there may be one household and one establishment at the same time, and the dwelling may consist of one room or more. And according to the census, every real estate unit inhabited at the time of enumeration is considered a dwelling, even if it was not originally built for housing, such as shops.
The types of dwellings are:
• A building originally constructed for the use of households like villa or popular house.
• Part of a building, such as an apartment, a floor, or a separate room (such as rooms built on rooftops).
• A mobile building, such as the tent, the nest, and the barn.
• A building that is occupied at the time of enumeration by a family and is no longer a place of residence, such as a shop, factory, school, workshop, bakery, restaurant and many work sites in which its workers live.
2.3.1.14Household
A person or a group of persons – with or without kinship binding them to one another – who live within the sampled dwelling during the enumeration. The household includes:
- Saudi and non-Saudi nationals who usually live at the dwelling but were temporarily absent while the survey was conducted (abroad or in the kingdom). For example: businessmen, tourists, people who are travel for medication, students on scholarship beyond the borders of the kingdom.
- Individuals who usually live at the dwelling but have been absent while the survey was conducted for taking night shifts, such as guards, physicians, nurses, airport staff and fishers.
- Domestic workers such as servants, drivers and the like who are living within the sampled dwelling. These individuals may have separate living quarters withing the dwelling.
2.3.1.15Head of household
It refers to the person regarded by the household members as its chief member. Usually, she/he is responsible for the household and his/her age must not be under (15) years old. If the household consists of children and their mother, and they are cared for by a relative who does not live with them, such a relative shall not be deemed as the head of the household, nor shall she/he be recorded as one of its members, since she/he shall be recorded with his/her own household. In this case, the mother shall be deemed as the head of the household.
2.3.1.16Work
Work comprises any activity performed by persons of any sex and age to produce goods or to provide services for use by others or for own use. It includes five mutually exclusive forms of work:
- own-use production work, comprising production of goods and services for own final use.
- employment, comprising work performed for others in exchange for pay or profit.
- unpaid trainee work, comprising work performed for others without pay to acquire workplace experience or skills.
- volunteer work, comprising non-compulsory work performed for others without pay; and
- other work activities.
2.3.1.17Employed Persons
The LFS is concerned with measurement of employment, and not other forms of work.
Employed persons (15 years and over) who during a specified reference week:
- Worked for at least one hour in return for a salary or profit (in cash or in kind) as an employee, as an employer, or working for themselves.
- Or who assisted a family member for at least an hour, with or without pay, in any type of business or on a farm belonging to a family member.
- Or who were temporarily absent from their work during the whole reference week due to leave, sickness, or any other reason, and who will return to it again.
- Or individuals with seasonal jobs during the period that is considered off-season if they continue to perform some of the tasks and duties of the job.
The definition includes students, job seekers, retirees, housewives, etc. who worked for at least one hour for pay or profit during the reference week, noting that this does not include unpaid housework such as cooking and washing done by a housewife or household maintenance work performed by a family member.
2.3.1.18Unemployed persons
The unemployed comprise all persons of working age (15 years and older) who were:
- Were without a job or business during the reference period, i.e., were not in paid employment or self-employment
- Currently available for work, i.e., were available for paid employment or self-employment during the reference week or in the following two weeks; and
- Seeking work, i.e., had taken active measure during the reference week or the previous three weeks to seek paid employment or self-employment.
Future starters, that is, persons who did not look for work but have a future job start are also counted as unemployed.
2.3.1.19Unemployed persons with previous work experience
Unemployed persons (15 years and above) who at some prior time had been employed – that is previously had a paid job or business.
2.3.1.20Persons in the Labor force
The labor force (formerly known as the economically active population) is the sum of the number of persons employed and the number of persons unemployed. As such the labor force includes all persons contributing or wanting to contribute to the production of commodities and services during the survey reference period.
2.3.1.21Persons out of the labor force
Persons outside the labor force (formerly known as the Inactive Population) are persons 15 years and above, who are neither employed nor unemployed. Thus, people who are neither employed nor unemployed (outside the labour force) are not part of the labour supply. It includes persons who during the survey reference period: did not want to work for pay or profit; who wanted a job but did not actively search for a job; who wanted a job but were unavailable to take a job during the reference period or the following two weeks. Examples include students not wanting a job while studying, persons not available due to providing care to other family members (child-care or elder-care), pensioners who do not want to work for pay or profit, individuals who are unavailable because of disabilities. It includes persons who are on the margins of the labor force, for example discouraged workers who want a job but have given up looking because they believe no suitable jobs are available.
2.3.1.22Main occupation
The main type of occupation practiced by the employed person during the reference time. This depends on the specific duties or functions of the person’s job.
2.3.1.23Economic activity
The main activity of the establishment or business in which a person worked during the reference period. The branch of economic activity of a person depends on the characteristics of the economic unit in which the person works.
2.3.1.24Type of sector
A sector is the entity for which the employed person has been working according to the estimates of the labor survey; it is divided into:
- Public sector: it includes all government entities such as ministries, authorities, government institutions, municipalities, schools, universities, institutes, government hospitals, military sector, government banks like (social development bank, agricultural bank) and development funds. It also includes establishments that produce goods and services and with ownership of 50% or more by the government such as (Saudi Airlines, Saudi railways Organization, and ARAMCO).
- Private sector: it includes all establishments that work in commercial and productive businesses, and market- oriented services that are owned by companies or individuals (companies, institutions, shops, small enterprises…etc.) either formal or informal, organized, or unorganized. These establishments have with less than 50% government ownership. The institutional sector that includes all self-employed individuals and employers is the private sector.
- Agricultural sector: It includes the unorganized sector of farms, animal husbandry, and hunting activities owned by individuals and families. However, it does not include the organized sector of agricultural and animal husbandry activities owned by private companies.
- Non-Profit Organizations Sector: Non-governmental non-profit organizations and authorities which provide the community with goods or services for free or at a nominal price, such as charities and vocational authorities.
- Domestic Workers Sector: Individuals who provide a household with services for a salary and live with it, such as the female domestic worker, driver, gardener, and building guard who lives with in the household.
- Regional and international organizations and institutions.
- Other unclassified sectors.
2.3.1.25Indicator definitions
|
Indicator |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Unemployment rate |
The unemployment rate is calculated by expressing the number of unemployed persons as a percentage of the total number of persons in the labor force. |
|
Labor force participation rate |
An indicator that is calculated by expressing the number of persons in the labor force as a percentage of the working-age population 15 years and over. |
|
Employment-to-population ratio |
An indicator that is calculated by expressing the number of persons employed as percentage of the total population 15 years and over. |
|
Average weekly working hours of paid employees |
Measures the average weekly working hours of workers (15 years and over), which is the total number of working hours of employees divided by the total number of employees. |
|
Average monthly wage per paid employees |
An indicator that measures the average monthly salary of the employed persons with paid jobs (15 years and above), i.e., total monthly salary of employees divided by the total number of employees. This measure is based on only those employees reporting their salary. |
|
Youth not in employment, education, or training (NEET) |
This indicator presents the share of young people who are not in employment, education, or training (NEET), as a percentage of the total number of young people in the corresponding age group |
In reporting these indicators, GASTAT provides a breakdown for the following age groups of the population aged 15 and above: Youth (15-24), Core Working Age (25-54) and population age 55 and over.
GASTAT has relied on the approved formulas of the UN international standards that are compiled with the International Labor Organization (ILO). The indicators are calculated as follows:
|
Based on the international standards that Saudi Arabia is committed to, and applied to the G-20 countries:
|
2.3.1.26Introduction of new age groups for Labor Market reporting and analysis
Beginning with the Q3 2021 release, GASTAT introduced three age-groups of the population that are of analytical interest in the examination and interpretation of labor market conditions. These groups are:
- Youth, persons aged 15 to 24 years.
- Core working-age population, persons aged 25 to 54 years, and
- Persons who are 55 years and older.
Labor market conditions differ for these age groups. For this reason, these groups are of interest to policy makers in developing policies targeted to different segments of the working age population.
Youth: Within the youth group, one can define two sub-groups for which labor market conditions are markedly different.
- Youth (15 to 19 years). Many persons between 15 to 19 years of age are students. Those participating in the labor force, would typically be interested in part-time work, but there can be a temporary influx of students into the labor force in search of jobs between school terms.
- Youth (20 to 24). Youth aged 20-24 are a mixture of those still pursuing studies as well as youth who have completed their education and are making the transition into the labor force.
Core working age population: Persons aged 25 to 54 years.
Persons aged 55 and over: In this age group, there is declining participation in the labor force. As the age increases within this group, more persons have retired or withdrawn from the labor force. Persons still participating in the labor force in this age group are mostly employed persons, with few people looking for work. Those not working are mostly out of the labor force, i.e., not actively looking for work.
2.3.2Concepts related to administrative records available at government agencies
(Second source of Labor Market statistics)
2.3.2.1Workers (based on the administrative records)
All working individuals subjected to approved regulations and laws from the regulatory entities of labor market are registered in the administrative records. Workers can be classified in the administrative records based on the regulations and laws they are subjected to as follows:
- Saudi workers subjected to the laws and regulations of the civil services and working at all governmental institutions and bodies, in other words, workers who hold jobs that are considered within the general budget of the country, also subjected to the civil retirement system (males or females) employees, as well as non-Saudi contractors who fill these positions in accordance the regulations of non-Saudi employment.
- Participants on the job who are subject and regulations of social insurance as well as labor system, which includes Saudis and non-Saudis.
|
Data of workers in Labor Market statistics which were derived from administrative records do not include the following categories:
|
Domestic workers: non-Saudi workers of both genders who work in houses, including servants, cleaners, cooks, waiters, drivers, guards, nurses, and private teachers.
2.4Statistical classifications used
Classification is identified as an organized group of related categories which are used to collect data according to similarity. Classification is the base for data collection and dissemination in various statistical fields, such as: (economic activity, products, expenses, occupations, or health, etc.). Classifying data and information helps to put them in meaningful categories to produce useful statistics. In fact, data collection requires an accurate organization based on their common features to create reliable and comparable statistics. Labor market statistics are based on the international standards of data collection and classification and rely on the following classifications:
2.4.1National guide for countries and nationalities
It is an international and unified classification that covers countries and their affiliated territories and is based on ISO (country code 3166). The classification gives codes to countries and their affiliated territories. Using these codes and numbers instead of the country name is more beneficial for statistical purposes in which it saves time and avoids any errors. The classification is used in the Labor Force Survey to classify Saudi or non-Saudi individuals.
2.4.2Saudi classification educational level and field of study
GASTAT surveys, including the Labor Force Survey classify education activities and education levels of persons according to the International Standard for Classification of Education (ISCED11), the reference for organizing educational programs and related qualifications based on the education levels and fields. It covers all the educational programs, levels and methods, of learning as well as all the educational stages from kindergarten until higher education. Educational programs in the Kingdom have been mapped into the international classification, and this classification is used in the Labor Force Survey to classify individuals 15 years and above according to levels of education participation and attainment, and field of study for advance levels of education.
2.4.3Saudi classification of occupations
Occupation refers to the kind of work performed in a job. A job being all the tasks carried out by a particular worker to complete his or her duties. An occupation is a set of jobs that are sufficiently similar in work performed. Kind of work is described in terms of tasks, duties, and responsibilities. Occupations are generally homogeneous with respect to skill type and skill level.
ISCO is the statistical classification system used in the Labor Force Survey to classify jobs by occupation, based on information collected on principal responsibilities and duties of the job.
2.4.4The National Classification of the Economic Activities
The National Classification of the Economic Activities is based on ISIC4 international classification which is the reference of the productive activities. This classification is used in the Labor Force Survey to identify the main economic activity of the establishment or business where an individual works.
The branch of economic activity of a person depends on the characteristics of the economic unit in which the person works.
2.5LFS Questionnaire design
The LFS questionnaire has been prepared and designed by labor force survey specialists in the General Authority for Statistics (GASTAT). When designing the form, the international recommendations and standards issued by the International Labor Organization (ILO) of labor force surveys have been taken into consideration. The questionnaire was presented to the ILO experts during their visit to the Authority and to the relevant bodies as well to consider their feedback and observations. The questions were formed in a specified and unified way between researchers.
Some modifications were introduced to the LFS questionnaire when the data collection methodology was changed for Computer-assisted personal interviewing (CAPI) to Computer-assisted telephone interviewing (CATI), at the beginning of the COVID19 pandemic in 2020, when the conduct of household surveys via persons visits and face-to-face interviews was no longer feasible. The change to CATI mode of collection, with telephoning interviewing from a central call center necessitated changes to the questionnaire to reduce the interview length to make it more suitable to a telephone interview.
Since then, the LFS questionnaire has undergone a few incremental improvements. A number of these were to address recommendations stemming from the SMO audit of the survey in 2021. The most recent changes were introduced in Q4 2021 and continue to be used in Q2 2022.
A summary of the most recent changes is included in this section. The LFS is currently undergoing a transformation, and one element of the transformation will be to examine the need for further revisions to the questionnaire to bring it in alignment with latest ILO recommendations and International Best Practices of Eurostat, and other leading countries including the US, Canada, and UK, as well as to address any special requirements specific to the context of the KSA labor market.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
After the survey questionnaire was approved, it was converted into an electronic form that can be used for computer-assisted collection – whether CATI or CAPI. Currently data collection is via CATI and CAPI. CATI data collection is carried out in a centralized Call Center at GASTAT. A computerized data collection system has been developed which is characterized by the following:
- Ability of supervisors to Review the researcher's work on a sample basis.
- A telecommunications system (Cisco Jabber), that manages the telephone network and call features to facilitate contact with sampled households.
- Use of the electronic CATI LFS questionnaire, to collect high quality data, through use of data auditing and navigation rules (to automatically detect input errors and illogical inputs the moment the data is completed).
- Communication between the supervisory groups by sending and receiving notes with the researcher.
2.6Methodology for Development and Testing of Questionnaire changes
As described above, the Labor Force Survey questionnaire content is determined by GASTAT. The needs for introduction of new questions or changes to existing questions are considered to keep the LFS questionnaire aligned to ILO standards and guidelines, other international best practices, and to consider the information needs of government departments, the principal users of the data.
Questionnaire changes are thoroughly vetted and tested before being introduced, via the following procedures:
- Drafting of Questions. Questions are drafted for the identified new content areas. ILO standards and international best practices are considered in this step, while also consideration of what adaptations to the local KSA context may be needed.
- Cognitive Testing. Cognitive testing is carried out by the GASTAT Center for Questionnaire Development. A small sample of persons is chosen to participate in the cognitive testing. Often past survey respondents are chosen, with a profile that is relevant to the new questions under study. For example, if the questions pertain to informal work, persons who worked in jobs likely to be informal would be chosen for the cognitive testing. The cognitive testing methodologies involve use of experienced interviewers trained in the cognitive testing procedures. They ask the respondents the new questions, and then ask about the respondent’s understanding of the question, the information they were being asked to provide, and the ability or difficulties if any in providing the requested information (such as recall of information, etc.). Based on this feedback, modifications are made to the questions to make them clearer and easier to respond to.
- Development of CATI Instrument. The questionnaire changes are then specified to and implemented in the CATI version of the questionnaire by the IT department. The LFS department does desktop testing of the new instrument to confirm the logical flow and appearance of the questions is correct.
- Operational Testing. A small test of the new questionnaire is carried out on a sample of households. This tests all the operations involved in the collection and production of files for processing of the data. Analysis of the data is also carried out to verify that the responses to the questions are as expected. The operational tests are not large enough to detect differences in the data, for example between a previous and new version of the questionnaire, but they ensure that operationally the questionnaire changes have been implemented in accordance with specifications, and the new data are introduced without causing problems to existing collection and processing of the data.
2.7Questionnaire Changes introduced in Q4 2021
In Q4 2021, three changes were made to the questionnaire as follows:
2.7.1Job search
Persons without a job or business are asked questions on what actions they have taken to look for work or start a business within the reference week and previous three weeks. Beginning in Q4 2021, respondents are read a list of actions, and in turn answer yes or no to each. In the past, respondents were asked to “volunteer” what job search methods they engaged in. Both methods conform to ILO standards and definitions. The new method is designed to yield better data on the methods used which is of policy interest.
2.7.2Informal Work
In recent years, a new set of questions was introduced to measure informal work. This module has been included on an annual basis in the Q4 survey. Work has been done on the module to ensure that the questions comply with international standards then the set of questions were reintroduced in Q4 2021 and in all future quarterly surveys.
The questions are aligned to ILO concepts and definitions of informal sector and informal employment as follows:
- Employment in the Informal sector: workers whose job is at an enterprise in the informal sector, where the Informal sector comprises unincorporated enterprises that produce at least partly for the market and are not registered. It excludes households that produce exclusively for own final use, subsistence agriculture, construction of own dwellings, etc.
- Informal employment: Employees in a job not protected by national labor legislation such as: social security or pension scheme, and not entitled to certain employment benefits, such as paid annual vacation and paid sick leave. Also included are Entrepreneurs in a unit of production that is considered informal, where entrepreneurs refer to employers, members of producers’ cooperatives and own account workers (only if what is produced is for sale); and contributing family workers.
2.7.3Time related Underemployment
This is a measure of persons working part-time for economic reasons, who want to work extra hours for pay or profit, and who are available to work extra hours.
2.8Identifying required data from administrative records
The administrative records data (the second source of the labor market statistics): GASTAT publishes administrative-based data labor market compiled automatically from government entities. The data includes the main data of employees, as follows:
- Data from the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development (MHRSD): Includes data on employees subjected to Civil Service regulations and policies according to several variables.
- Data from General Organization for Social Insurance (GOSI): Includes data related to those who are registered and are working, who are
- subjected to GOSI’s regulations and policies according to several variables.
- Data from the National Information Center (NIC): It includes data related to domestic workers, according to several variables.
These data are published on a quarterly basis in a separate release from the LFS survey results.
2.9Coverage
2.9.1Spatial coverage
The labor market statistics are produced for the 13 Administrative Regions of Saudi Arabia. The regions are Riyadh, Makkah, Madinah, Qassim, Eastern Region, Asir, Tabuk, Hail, Northern Borders, Jazan, Najran, Al-Baha and Al-Jouf.
For the Labor Force Survey, the sample is designed to include a representative sample from each region with a sample size sufficient to produce reliable estimates for the region (see section 2.11.4). The sample sizes for the smaller regions were increased during the current redesign to improve the reliability of the survey estimates for these regions.
The administrative-based data include the entire population of Saudi Arabia whose data is documented in the records of relevant government entities, and these are also released with breakdowns by the 13 Administrative Regions.
2.9.2Temporal coverage
The Labor Force Survey data (the first source of the labor market statistics) are based on household members, their demographic, social and economic characteristics, as follows:
- Data on the roster of household members and their demographic characteristics is based on the reference week for the sampled dwelling.
- Data to classify persons as employed or not are based on the reference week
- Data on job search activity are based on the reference week and the previous 3 weeks.
- Data on employment availability is based on the reference week and the following two weeks
- Data of enrollment in training programs is based on the reference week.
The data from administrative records (the second source of the labor market statistics) is based on the last day of each Gregorian quarter of each year.
2.10Labor Force Survey Statistical framework
- The LFS sample frame comprises a list of all residential dwellings in KSA constructed from the 2022 Census of Housing and Population. The frame includes identification of the building, dwelling identifiers, and for the dwellings occupied in 2022 when the list was prepared, the head of household telephone number and head of household ID of occupied residential dwellings.
- The lists, maps and analytical specifications of the units have been developed to select a sample of dwellings.
- The required metadata has been identified to create the statistical framework and the testing framework and verify its validity and use for the current survey cycle.
The target population for the KSA Labor Force Survey (LFS) remains the non-institutional civilian population (15 years and over) residing in private dwellings. The eligibility criteria for the non-Saudi households and individuals is that they have been in the Kingdom for at least six months. It should be emphasized that the sampling unit is the dwelling and the household occupying the dwelling is the unit of observation, i.e., data are collected from the households occupying the sampled dwelling.
2.11Sample Design
The Labor Force Survey sample was redesigned based on results of the 2022 Census and the introduction of the new sample design (the 2022 Design) began in Q4 2022. The sample rotation feature of the sample with four rotation groups that was introduced in Q4 2021 has been maintained without any change.
Major features of the redesigned sample are described below:
2.11.1Adoption of dwelling as second-stage sampling unit
The choice of second-stage sampling unit is a fundamental feature that has implications not only on the design of the sample but also on the data collection procedures.
In the old design (prior to the 2021 redesign), household was the second-stage sampling unit. Households are the residents of occupied dwellings. However, if the household and not the dwelling is the sampling unit, when a household moves, it should remain in the sample. Movements of households since the time of creation of the frame and when a household gets sampled create problems being able to contact the household, as well as complexities in estimation, as household may become stratum jumper – they may no longer belong to the stratum in which they were originally selected. Also changes in household composition over time adds to the complexity of this approach. As a fundamental change in the sample design, the dwelling was adopted as the second-stage sampling unit during the 2021 redesign. This feature of the LFS design has been maintained during the 2022 redesign.
2.11.2Stratification
The 2021 Sample design, based on 2020 pre-censal canvassing data, was implemented in Q4 2021 and had 350 design strata. The 13 Administrative Regions were sub-divided based on the degree of urbanization (urban, semi-urban, rural) resulting in 55 primary strata. (These 55 primary strata were the same as the final design strata in the pre-transformation 2010 design.) These 55 primary strata were then further sub-divided into 350 design strata based on geographical hierarchy.
In the 2022 Sample design, based on results of the 2022 Census, 9 large cities and 6 special territories were included in addition to the 13 Administrative Regions as part of the primary stratification. These 9 large cities and 6 special territories were included because survey estimates are to be produced for these subnational areas. This resulted in 29 geographic areas (these are 29 geographic areas and not 28 because the Al Ula territory is in two administrative regions). The 29 strata were sub-divided based on the degree of urbanization (urban, semi-urban, rural) resulting in 59 primary strata.
A primary benefit of stratification is that it eliminates the between strata variation in the survey estimates. The ideal in stratification is to have homogeneity within strata and heterogeneity between strata for the characteristics of interest. To the degree to which that is achieved, stratification is a very powerful means of reducing the variance in the survey estimates.
To carry out “optimal” stratification, one would want to form strata using detailed Census data on the characteristic of the population. Since the latest Census information became available from the 2022 Census of Population and Housing, we made use of the Census information to form secondary strata. The 59 primary strata were sub-divided into 447 secondary strata based on the population characteristics collected during the 2022 Census of Population and Housing. The population characteristics used for secondary stratification can be summarized as:
- Person Characteristics
- Demographic: Age, Gender, Nationality, Marital Status, etc.
- Socio-economic: Education, Income
- Labor Force: Employment by Industry, Employment by Occupation, Employment by Sector
- Household Characteristics:
- Distribution of households by size
- Nationality of head of the household
- Dwelling Characteristics
- Type of dwelling
- Dwelling Tenure (Owning vs. Renting)
An added benefit of the geographic stratification adopted is to ensure a good geographic distribution of the sample.
2.11.3Allocation of the Sample
In the 2021 Sample design, the allocation of the sample was a compromise between requirements for national and regional data. The optimal allocation for national estimates is a proportional allocation where the sample size for each region is proportional to its share of the total population of the Kingdom. While best for national estimates, such an allocation is not good for regional estimates, as smaller regions would not have sufficient sample sizes to yield reliable data. A sample allocation that ensures all regions have a sufficient sample to yield reliable estimates was needed, and this compromise was achieved using the square root allocation across regions. It was observed that this compromise allocation did not allocate sufficient sample to the smaller regions. Moreover, adequate sample sizes had to be allocated to the sub-national areas, which included 9 large cities and 6 special territories.
In the 2022 Sample design, the desired improvements in regional and subnational estimates were achieved in two steps. First, a power allocation with power = 0.4 to allocate the sample to the 13 regions. This satisfied the sample size requirement for the 13 regions and all 9 large cities, by allocating more of the sample to smaller regions than the previous square root allocation. But this allocation did not satisfy the sample size requirement for all 6 special territories. The sample size requirement was satisfied for only 2 out of the 6 special territories. In the second step, the sample for the remaining 4 special territories was augmented to achieve the required sample sizes. This resulted in a total sample of 96,000 dwellings as compared to 80,000 dwellings for the previous redesign. Thus the overall sample was increased by 20 percent from the 2021 sample design. The sample allocation to strata within these areas was based on proportional allocation.
2.11.4Determination of Sample Size
In the previous redesign (i.e., 2021 redesign) the sample size was 80,000 dwellings. As mentioned above, the sample size was increased from 80,000 dwellings to 96,000 dwellings to produce survey estimates with required margin of sampling errors both for the regions and the additional subnational areas consisting of 9 large cities and 6 special territories.
2.11.5PSUs and Cluster size
As for the 2021 Sample Design, Census enumeration areas (EAs) were taken as PSUs for the redesigned sample, and the large EAs were split into multiple PSUs such that the probability of selection of the PSUs is always less than 1. The average cluster size in both the 2021 and 2022 Sample Designs was from 13-13.5 sampled dwellings per PSU.
2.11.6Sampling of Primary Sampling Units (PSUs)
The sampling of PSUs was done by using randomized probability proportional to size (RPPS) systematic method of sampling within each stratum using the sampling rate determined from the sample allocation. It should be noted that the random start used for systematic sampling determines both the PSUs to be selected as well as the dwellings to be selected within PSUs. New samples of dwellings within PSUs are selected as needed simply by advancing the random start.
Under the 2022 Sample design 7,100 PSUs were selected as compared to 6,016 for the 2021 Sample design.
2.11.7Sample Rotation and Assignment of Rotation Groups
Sample rotation was introduced under the 2021 Sample Design, and was continued unchanged in the 2022 Sample Design. Under the rotation scheme adopted, dwellings remain in the sample for 4 consecutive quarters, and each quarter 25% of the sample consists of birth dwellings in the sample for the first time, and 75% of the sample are retained dwellings – that is dwellings already sampled from the previous quarters.
The principal rationale for a rotating sample design is to reduce the variance of estimates of quarter-to-quarter changes. In any continuous survey, the estimates of change from one time period to the next are one of the important, if not the most important, estimates.
The rotating sample design reduces the variance in the estimates of change, due to the positive correlation in responses of the same respondents in the overlapping sample from one quarter to the next.
Reduction of the variances of estimates of change increases the power of the survey to detect statistically significant changes from quarter to quarter and also reduces the volatility and quarter-to-quarter fluctuations in the time series.
To implement sample rotation, sampled PSUs within strata were assigned a rotation number of 1,2,3 or 4 in a balanced way, which determine the sample rotation. The number of PSUs sampled from a stratum is always a multiple of 4, and each rotation group is assigned the same number of times in a stratum such the sample yield is as equal as possible among the 4 rotation groups.
Once the sample design is fully “phased-in” in Q1 of any year, dwellings from the previous quarter with rotation number 1 will be dropped and replaced by a new sample of dwellings with rotation number 1. Similarly, in Q2 of every year, a fresh sample of dwelling with rotation number 2 will be introduced (replacing the rotation number 2 dwellings from the previous quarter which “rotate out” of the sample.). Similarly, rotation will take place in Q3 for rotation group 3 and in Q4 for rotation group 4.
2.11.8Phase-in of Sample rotation
Q4 2022 represented the first quarter for the new sample design – and the start of a phase-in of the rotation design. In Q4 2022, a fresh sample of dwellings was introduced for all rotation groups: 1,2,3 and 4. In Q1 2023, dwellings from the Q4 sample in rotation group 1 will be dropped and replaced by a fresh sample of dwellings for Q1 2023. The sampled dwellings for the other rotation groups will remain the same. Thus, there will be a 75 percent sample overlap between the Q4 2022 and Q1 2023 quarterly samples.
This pattern will continue each quarter in 2023, , with the sample from one rotation group being replaced each quarter. The sample will become fully “phased-in” in Q3 2023 when 25% of the sample will be new dwellings, 25% will be in the sample for the 2nd time, 25% will be in the sample for the 3rd time, and 25% will be in the sample for the 4th time which will be the last interview for the households occupying these dwellings.
2.11.9Continuous Data Collection
2.11.9.1Objectives of Continuous Data Collection
Continuous Data Collection (CDC) represents one of the major changes introduced during the LFS transformation. The principal objective of Continuous Data Collection is to spread out the data collection across the weeks of the quarter, to improve the representativeness of the sample in a time dimension. Under the 2022 Design, the LFS remains a quarterly survey, with a rotation pattern optimized to improve the reliability of estimates of quarter-to-quarter change, by having a 75% overlap in the sample of dwellings between successive quarters. Prior to adoption of CDC, LFS data collection took place during a 3-week period within one month per quarter. Under CDC, data collection is spread out over 12 weeks per quarter, with selection of a sample for each week that is a representative sub-sample of the overall LFS quarterly sample. That is, the quarterly LFS sample of 96,000 unique dwellings, is divided into 12 samples, each of 8,000 unique dwellings.
2.11.9.2Methodology for partitioning the LFS quarterly sample into 12 representative weekly samples.
The partitioning of the overall LFS sample each quarter into 12 representative weekly samples was done independently of rotation group. In effect, an ordered list of LFS sampled dwellings per quarter was systematically assigned a week number between 1 and 12, to derive the weekly samples.
In this fashion each weekly sample is a representative 1/12 sample of the overall quarterly sample.
2.12Summary of main features of the redesigned LFS Sample
Table 2-1 below summarizes the main features of the 2022 LFS sample design introduced in Q4 2022, based on results of 2022 Census, as compared to the 2021 Design based on Pre-censal dwelling lists and introduced in Q4 2021.
|
Table 2-1 Key features of the 2022 Labor Force Survey Design |
|
Key design features |
2021 Design |
2022 Design |
Impact / Rationale |
|
|
350 |
447 |
|
Immediate impact, Q4 |
|
13-13.5
|
|
||
|
Square Root Allocation |
Power Allocation with Power = 0.4
Further oversampling of sub-national areas. |
|
|
|
80,029 (DUs) ~62,000 (HHs)
|
96,000 (DUs) ~82,000 (HHs)
|
||
|
Primary: PSU (EA/Split-EA) Secondary: DU Observation Unit: HH |
|
||
|
25% rotation introduced in Q4 2021
|
|
Cost efficiency gains seen in Q1 onwards Impact, Q1 2023 |
|
|
Yes, in Q4 2021 and Q1 2022 |
No |
|
|
|
Yes, from Q2 2022
|
|
||
|
No |
Yes, beginning in Q1 2023 |
|
|
|
EA – Census Enumeration Area, HH – Household, DU – Dwelling Unit |
||||
|
Table 2-2: The Sample Sizes by Regions – Redesigned Sample and Old Design Sample |
||
|
Region |
Sample Size |
|
|
Redesigned Sample (2022)
|
Redesigned Sample (2021) (Dwelling Units) |
|
|
Riyad |
12,652 |
12,103 |
|
Makkah |
13,650 |
13,531 |
|
Madinah |
10,296 |
6,838 |
|
Qassim |
6,170 |
5,373 |
|
Eastern Region |
13,582 |
9,450 |
|
Aseer |
7,434 |
6,978 |
|
Tabuk |
6,133 |
4,537 |
|
Hail |
4,558 |
3,649 |
|
Northern Borders |
3,299 |
2,464 |
|
Jazan |
5,961 |
5,377 |
|
Najran |
4,561 |
3,191 |
|
Al Bahah |
3,814 |
3,482 |
|
Al Jouf |
3,903 |
3,100 |
|
KSA |
96,013 |
80,072 |
|
Sample units in the Labor Force Survey: The Primary Sample Unit (PSU) is the enumeration area (EA) or a split of the enumeration area when the enumeration area size is large. The PSUs are the first stage units in the sample design. The dwellings within the PSUs are the second stage and the final sample units. The households living in the dwellings are the observation units for the survey. These features of the sample design remain unchanged between the 2021 sample redesign and the 2022 sample redesign. |
3.Third stage: Organization
This is the last stage of the preparation that precedes the process of household contacts and data collection. The work procedures required for the preparation of the labor market statistics have been prepared in this stage. It will begin from the next stage "collection stage" and will end with the “assessment stage”. In addition, the procedures are organized and collected, and its appropriate order is determined to reach a methodology that achieves the objectives of the labor market statistics. At this stage, the procedures that were done in the preparation of the previous version of the labor market statistics were reviewed to develop the work procedures in this version. These procedures were also described and documented to facilitate the updates in the future cycles. Furthermore, the statistical work procedures were tried and tested to ensure that they meet the requirements of the preparation of the labor market statistics in its final form. Then, the procedures of the statistical work are approved, and the road map of the implementation is developed.
Testing the efficiency of input systems and the process of transmission, synchronization, and review of data, which is carried out through tablets or desktops of the labor force survey, is one of the most important procedures at this stage.
4. Fourth Stage: Data Collection
4.1Labor Force Survey Data Collection
4.1.1Multi-mode Data Collection
Since Q2 2022, the data collection methodology for the LFS has followed a multi-mode CAPI/CATI methodology, where CAPI is used for birth dwellings, and for follow-up of both CAPI and CATI no-contact and nonresponse cases from the previous quarter, and where CATI is used for previous quarter respondent households. These general rules had to be modified for introduction of the 2022 sample redesign in Q4 2022 (see section 4.1.3).
4.1.24.1.2 CAPI Collection
4.1.2.1Classification of dwelling status
The first step in CAPI collection is to determine the current status of sampled dwellings. The CAPI researcher visits each sampled dwelling in his/her assignment to determine its current status as occupied, vacant, under construction, demolished, or otherwise out-of-scope for the LFS. Only occupied residential dwellings containing one or more usual residents of KSA are in-scope for the LFS. All other dwellings are out-of-scope – that is vacant, under construction, demolished dwellings, as well as occupied dwellings where all occupants are not part of the LFS target population – for example all occupants are foreign diplomats or their family members, or the dwelling is used solely for business purposes and no persons reside there.
Distinguishing between occupied and vacant dwellings may require up to three visits to a dwelling to find someone at home, or signs of life such as lights, presence of a vehicle, sound of individual inside the dwelling, etc. If there are no signs of life after 3 visits, the dwelling is classified as vacant.
4.1.2.2Completion of LFS questionnaires
For occupied in-scope residential dwellings, the CAPI researcher completes an LFS interview, including verification of head of household ID and telephone number, completion of a roster of household members, and completion of the LFS questionnaire for each usual resident aged 15+. Proxy responses are permitted, and usually the head of household responds for his- or herself and for other household members.
CAPI questionnaires are sent back to headquarters daily. There they are merged with CATI questionnaires completed each day, to constitute the households surveyed for each day.
The CAPI mode of collection has contributed to improving the coverage and response rates for the LFS, by first identifying all occupied dwellings, and by providing up-to-date contact information for them. International experiences are that face-to-face data collection yields improved response rates compared to telephone collection (CATI), and this has also been observed in the KSA LFS.
4.1.3 CATI collection
As noted, CATI data collection is carried out for non-birth sample cases which were respondent in the previous quarter. Each quarter the CATI cases comprise – (i) previous quarter CAPI respondents (mostly birth sample respondents from the previous quarter), and (ii) previous quarter CATI respondents.
CATI researchers work in the CATI call center. An intermediate step before CATI collection involves obtaining further information from NIC on the household members, based on the head of household ID. This procedure helps to ensure completeness of the roster of household members, and provides some of their demographic information, so that it does not have to be collected directly from respondents, thereby reducing the length of interview and respondent burden.
When a researcher finishes one case (a contact attempt or an interview with a household), he/she is assigned the next household in the queue maintained by the case management system. When a household is contacted, the researcher follows a protocol that includes self-introduction, clarifying the reason for the call, giving an overview of the survey and its objectives, and obtaining the respondent’s permission to continue with the interview. If the respondent is unavailable to complete the questionnaire when initially contacted, a best time to call back is obtained.
4.1.4 Data Collection for Introduction of Redesigned sample in Q4 2022
With the introduction of the 2022 Sample Redesign in Q4 2022, a fresh sample was selected from the new frame and sample design. Hence all sampled dwellings were birth cases. The normal procedure of allocating birth cases to CAPI collection could not be followed, as the CAPI field capacity existed to handle only about 40% of sampled cases (the normal 25% birth cases and the follow-up of cases where an interview was not completed in the previous quarter).
The Q4 2022 sample was allocated to achieve 40% CAPI and 60% CATI cases for each sub-national area as follows:
- For sampled dwellings contact information namely the head of household ID and telephone number were obtained from the 2022 Census database. Cases where the contact information was missing in the Census were assigned to CAPI.
- For dwellings with contact information, priority for CAPI collection was given to dwellings which will remain in the sample the longest before rotating out, to maximize benefits of the CAPI first contact for subsequent interviews. First priority for CAPI were those with rotation number 4, which will remain in the sample until Q3 2023; and next priority was given to dwellings with rotation 3. These criteria were applied in a balanced fashion geographically.
- Once 40% of dwellings were assigned to CAPI via steps (i) and (ii), remaining cases were assigned to CATI collection.
Application of these rules meant that the CATI cases (60% of the sample) were “cold” CATI interviews: that is, where there was no prior face-to-face contact with the household. Despite sending an introductory letter from the president of GASTAT to households via text messaging, the response rates from “cold” CATI data collection are lower than that achieved under the normal mixed mode of CAPI/CATI used for the LFS, where the first contact is face-to-face. Impacts of the Q4 2023 “cold” CATI collection were seen in Q4 2022 response rates, and will continue to be seen but in diminishing amounts in response rates in Q1 2023 and Q2 2023, as households initially contacted via “cold” CATI continue to remain in the sample.
4.1.5Implementation of Continuous Data Collection in Q1 2013
CDC has required the adoption of fixed reference periods for the LFS, replacing the “sliding” reference periods previously used. For example, the principal reference period for the LFS is that used to determine if a respondent is employed or not. Previously that reference period was 7 days prior to the date of interview. Hence it varied across sampled dwellings depending on their date of interview. Under CDC, the reference period has become a fixed week – the reference week. Each weekly sample has a fixed reference week, which always applies to that sample – regardless of when the interview takes place for a given household.
In the LFS questionnaire, there are a number of reference periods, which all become fixed under CDC, and are a function of the fixed reference week.
In addition to the adoption of fixed reference periods, under CDC there is a fixed primary collection period, and follow-up period for each weekly sample. The primary collection period is usually the week preceding the reference week, and during this week the main emphasis of data collection will be on the new cases for the weekly sample. Around major public holidays, adjustments are made to the primary collection period to avoid data collection on official dates of national holidays. The follow-up collection period for each weekly sample is typically the week after the primary collection period, to allow for nonresponse follow-up of the previous week’s sample. It should be noted that every week, interviewers therefore need to do the primary collection for the current week’s sample, and non-response follow-up for the previous week’s sample. When doing the nonresponse follow-up, the reference period does not change – e.g. it refers to a week that is typically 2 weeks in the past, rather than one week in the past.
Table 2.3 shows the reference periods and collection periods under CDC, compared to what existed prior to adoption of Continuous Data Collection on Q1 2023.
4.1.6Specification of sampled dwellings, collection periods and reference week
The LFS sampling system provides to CAPI and CATI Case Managements Systems a specification of the quarterly LFS sample at the dwelling level, for all dwellings – both birth and subsequent dwellings, providing the week number (and month number) for each dwelling, as well as the start and end dates for: primary collection period, follow-up collection period, reference week, and reference period for active job search. The full monthly samples are loaded into Case Management Systems for CATI and CAPI respectively in advance of data collection for each month.
For CAPI, the monthly sample is used in the Candidate system to prepare assignments for each researcher. The cases for the entire month are uploaded to tablets of the CAPI researchers. Each week, the new weekly sample cases are activated on the tablets, and any outstanding cases which were not completed during the follow-up period just ended are closed out, transmitted back to headquarters, and removed from the tablets. Similarly for CATI, the new cases are activated at the start of each week, and old cases whose follow-up collection period has ended are closed out and removed from the data collection system.
4.1.7
|
The training programs that have been provided to researchers assigned to all Labor Force Survey data include conceptual and practical lectures on the technical, administrative and awareness materials used in the data collection processes. Researchers are also introduced to the survey objectives and data collection method. The training programs also include a detailed explanation of all the questionnaire questions, and the technical tasks, and administrative, as well as training on methods of communicating with data providers and how to submit questions in record time. |
Recruitment of researchers
The candidates working as researchers (interviewers), who contact the households to collect data for the Labor Force Survey, were selected according to several practical and objective criteria related to the nature of work, such as:
- Education level.
- Previous experience in labor force survey and other household surveys.
- Personal qualities, such as: good conduct, medical and psychological fitness with no sensory disability.
- Not less than 20 years old.
- The candidate must pass the training program of the Labor Force Survey.
4.1.8Training of Researchers
All candidates (employees of the authority, collaborators from employees of some government agencies) were qualified and trained to work in collecting survey data through special training programs, according to the following:
- Holding a training program for researchers that included providing guidance and awareness lectures, during which the instruction manual is explained, the survey objectives and data collection method are defined, and a detailed explanation of all the questionnaire questions.
- Two separate trainings were conducted for CATI and for CAPI.
- Conducting a practical application on how to complete the CATI and CAPI survey form.
The performance of the researchers was also tested during the training, their performance was evaluated, and the extent of their understanding of the questionnaire was verified before starting the communication and data collection process.
4.1.9On-line edits during data collection
Edit rules are built into the questionnaire to ensure the consistency, accuracy and logic of the data collected. These were built by linking the logical relationship between the answers to different questions and variables to help the researcher to detect any error directly when completing data with the household. For example, if a person with primary level of education later reports an occupation that requires advanced education, such as a brain surgeon, this triggers an error message, which needs to be resolved between the researcher and respondent before continuing with the interview. Such on-line editing can significantly improve the quality of the data collected by resolving discrepancies directly with the respondent.
4.1.10Monitoring and Supervision
Calls with households are recorded, and supervisors listen to a sample of calls to ensure that researchers are following proper procedures in asking the questions and in correctly completing the questionnaire based on the responses provided. Ten percent of households are monitored in this fashion. Feedback is provided to researchers by the supervisors, to improve their work. In cases where the interview has not been conducted correctly, then the household is recontacted to clear up problems with the original interview.
In addition to this procedure, several reports are produced giving rates of missing or erroneous data by researchers. These are used in training of researchers. Researchers with consistent performance problems are replaced.
4.2Access to data from administrative records (second source of Labor market statistics)
GASTAT has coordinated with the government entities concerned with the Labor market to obtain data on Labor market statistics. Such data include data of workers, based on data of administrative records. These data are preserved in the databases of the Authority and are audited and reviewed according to the scientific statistical method and generally quality criteria in coordination with the source of the data.
5 Fifth Stage: Tabulation
During this stage, raw data are tabulated based on the classification and coding inputs completed during the data collection process, according to the Saudi Standard Classification of Occupations is based on the International Standard Classification of Occupations (ISCO-08); The National Classification of Economic Activities, based on the International Standard Industrial Classification of Economic Activities (ISIC4), the Code of Countries and Nationalities According to Country Codes – ISO 3166; and the International Manual, and Majors and Education Levels Manual based on (ISCED11). During Tabulation process, other classifications and coding are also used, such as: data distribution at administrative regions level, qualitative and descriptive classification in terms of gender determination, individual’s marital status, and quantitative classification such as income groups.
Specialists of the Labor Force Statistics Department have processed and analyzed data in this stage, and this step was based on the following measures:
- Sort and arrange data in groups or different categories in a serial order
- Summarize detailed data into main points or main data
- Linking between many parts of data and make them connected
- Process incomplete or missing data
- Process illogical data
- Weighting of Survey Data
- Production of Quality measures
- Organize, display, and interpret data.
5.1Weighting of Survey Data
After processing the data collected from the respondent households, the next step is the weighting of the survey data. Weighting is a critical step required to produce survey estimates. Survey estimates, for a characteristic of interest, are generated by weighted counts of respondents possessing the characteristic.
There are four steps involved in the weighting of the survey data as follows:
5.1.1Design weight
Design weights account for the different probabilities of being sampled. The sample design is self-weighting at the level of Administrative Region and the 4 special territories for which the sample size was augmented to satisfy required precision criteria. The sampling rates for the 9 large cities and 2 special territories are the same as for the corresponding Administrative Region. This means that all dwellings in the Administrative Region and the 4 special territories have the same probability of being selected in the sample. The design weight is the inverse of the probability of selection. That is if the probability of selection in a region is 1/200, then the design weight for the Administrative Region would be 200. All respondent households (and persons within) in the region (or subnational area) receive the design weight for the region (or subnational area).
5.1.2Nonresponse weights
All surveys experience nonresponse. Nonresponse is usually compensated for by means of a weight adjustment. The nonresponse adjustment factor is typically applied at a low level such as the PSU, and this is the level at which it is applied in the Labor Force Survey. Within a PSU, the nonresponse adjustment factor is simply:
Nonresponse adjustment factor = (number of in scope households in the PSU) / (number of responding households in the PSU)
If the nonresponse adjustment factor in a PSU is greater than 3, then the cell for doing the non-response adjustment is collapsed. A nonresponse adjustment factor of 3 is equivalent to a 33% response rate in the cell. In such cases it is better to spread the nonresponses adjustment over a wider sample, rather than have high weights within the PSUs in question. In such cases, the nonresponse adjustment cell is collapsed into two cells for the entire stratum, defined by households with odd versus even rotation numbers. The adjustment factor for each of these cells was defined similarly as the number of in scope households in the cell divided by the number of respondent households in the cell.
5.1.3Calibration weights
Calibration is the final step in the weighting. In this step, the weights of sample are adjusted so that the survey estimates of population agree with external population estimates. The independent population estimates used in the Q1 2023 were based on 2021 Mid-year population estimates produced by the Population and Housing Division. Population estimates based on the 2022 Census had yet to be finalized and released.
As part of the 2022 LFS transformation, since Q2 2021 a raking ratio methodology has been used for the final stage calibration step. In Q4 2022 and Q1 2023 the following population controls were used in the calibration step:
Dimension 1 (National Controls):
Cross-classification of 5-year Age-Groups × Gender × Nationality,
Dimension 2 (Regional Controls):
Administrative Region (13) × 3 Age-Groups (less than 15, and 15-24, 25+) × Gender × Nationality
For dimension 1, the 5-year age groups, are as follows: {0-4, 5-9, 10-14, 15-19, 20-24, 25-29, 30-34, 35-39, 40-44, 45-49, 50-54, 55-59, 60-64, and 65+}.
The calibrated weights (also known as final weights) are assigned to the persons enumerated from the respondent households. The final weights are then used to create tables of the required indicators.
The raking ratio methodology works by first applying the national controls. The resultant weights are input into the next step – the application of the regional controls. Alternative application of the controls to the interim weights is applied iteratively until the calibration weights converge to the point of agreement within a specified level of tolerance with both sets of population controls.
5.1.4 Independent Population Estimates used in Calibration
The underlying assumption in the variance estimation is that the independent population estimates are free of error. This is a very strong assumption. The Population and Housing Division of GASTAT is responsible for population estimates and is researching the development of improved estimation methodologies making greater use of administrative data.
The population estimation methodology applied from Q2 2022 to date is based on the Cohort Components Method. This method starts from population of the previous midyear (midyear 2021) then adding birth and net migration flow minus the deaths that occurred between the two quarters. This is applied at the national level. To derive estimates at the regional level, a ratio method is used by region, age group, nationality, and gender. The GASTAT website provides more details on the population projection methodology.
5.2Quality measures for LFS survey data
5.2.1Estimation of sampling errors
After weighting, the next step is to produce estimates of sampling errors. These are calculated using replication methodologies. Procedures to apply these methodologies exist in statistical software tools such as SAS.
In Q2 2021 and Q3 2021 the jackknife method of replication was used, where the number of replicates was equal to the number of PSUs. From Q4 2021 and onward, with the introduction of the new design, there are far more PSUs making the jackknife method computationally cumbersome. Hence the BRR method has been adopted where the number of replicates needed is 352—the smallest multiple of 4 greater than or equal to number of strata (350). The BRR method will be continued for estimation of variance for Q4 2022 and the subsequent quarters. The number of replicates for the redesigned sample will be 448 – the smallest multiple of 4 greater than or equal to number of strata which is now equal to 447.
Several quality indicators including Coefficients of Variation (CVs), design effects, confidence intervals, response rates and slippage rates are being produced for the key survey indicators.
5.2.2Non-sampling errors
Two quality measures of potential non-sampling error are produced. These are:
Response rate - Percentage of eligible households which successfully complete the questionnaire. A High response rate indicates that the potential for non-response bias is small – and that estimates are more representative for underlying population.
Slippage rate - Defined as the percent difference between the population used as control total for calibration and the corresponding population estimated from the LFS without calibration. A positive slippage rate is a measure of the under-coverage of the LFS relative to the external population estimate, and should not be more than 20.0 percent. High slippage rate indicates that there is a high potential bias due to undercoverage. It should be noted that slippage rate is a relative measure of coverage error, where coverage errors can occur in either the LFS, the independent population estimates, or both.
6 Sixth Stage: Revision
First: Data Outputs Validation
In addition to the data processing and tabulation in the fifth stage to check their accuracy, all the outputs are stored and uploaded to the database after being calculated by GASTAT to be reviewed and processed by specialists in Labor Force Statistics through modern technologies and software designed for this purpose.
Second: Dealing with confidential data
According to the Royal Decree No. 23 dated 07-12-1397, data must always be kept confidential, and must be used by GASTAT only for statistical purposes. Therefore, the data are protected in the data servers of the Authority.
|
Under no circumstances can that be allowed to disclose about any data of the households or their members. It is worth mentioning that the publications are statistical tables at the level of Saudi Arabia and its administrative regions and main cities by demographic characteristics. |
7 Seventh Stage: Publication
First: Preparation and Process of the Results Designed for Publication
During this stage, GASTAT downloaded the data’s results from the database of surveys of Labor force. Moreover, it organized and reviewed the data of administrative records included in the Labor
Market Statistics Publication. Then, the publication tables and graphs of data and indicators, metadata, and methodology were prepared and processed to be prepared in both languages English and Arabic.
Second: Preparing Media Kit and Announcing Publication Date
The publication date of the Publication is already set up by GASTAT on its official website at the beginning of the Calendar Year. During this period, the Authority is preparing the media kits to
|
GASTAT uses the Special Data Dissemination Standard (SDDS) issued by the International Monetary Fund. According to this Standard, all statistics agencies are required to publish data on employment, unemployment, and wages on a quarterly basis, and with a delay of not more than one quarter (90 days) after the end of the reference quarter. If the data are from different source, they may be published in a different frequency. |
announce the date of releasing the Publication through media in addition to its various platforms in social networking sites. The Publication will be published firstly on GASTAT’s official website in different formats, such as open data in Excel format to be easily reached for all clients and those who are interested in the Labor market in general. It will be uploaded on the website’s statistics library as well.
Third: Communicating with clients and providing them with the Publication’s results
One of GASTAT’s objectives is to better meet its clients' needs, so it immediately provides them with the Publication’s results once the labor Market Statistics Publication is published. It also receives questions and inquiries of the clients about the Publication and its results through various communication channels, such as:
- GASTAT’s official website www.stats.gov.sa
- GASTAT’s official e-mail address info@stats.gov.sa
- Client Support’s e-mail address cs@stats.gov.sa
- Official visits to GASTAT’s official head office in Riyadh or one of its branches in Saudi Arabia.
- Official letters.
- Statistical telephone (920020081)
8 Eighth Stage: Evaluation
All GASTAT’s clients who used the results of the Publication will be contacted again to assess the entire statistical process. This is done for improvement purposes to obtain high-quality data. The improvements include methodologies, procedures and systems, statisticians’ skill level, as well as statistical work frameworks. The participatory stage is carried out with the data users and Authority’s clients according to the following steps:
First: Collection of Measurable Assessment Inputs
The most important comments and notes are collected and documented from their sources in different stages, for example comments and notes given by data collectors and their supervisors. Also, notes written by specialists responsible for reviewing, auditing, and analyzing data collected from the team or administrative regions. Finally, comments and notes collected and documented by data users after publishing the Publication, or social media comments and clients’ feedback that is sent to the Authority through its main channels.
Second: Assessment
The assessment is done by analyzing collected evaluation inputs and comparing the results of this analysis with the ones expected previously. Therefore, a few possible improvements and solutions are identified and discussed with specialists, experts, and concerned partners of labor market community. During this step, clients' performances, and satisfaction levels of using the results of labor market statistics are measured. It is worth mentioning that based on these procedures, the recommendations for obtaining high quality data for the next labor market statistics are agreed upon.
9 Ninth Stage: Management
It is a comprehensive stage required to carry out each phase of the labor market statistics production. During this stage, the plan of production is developed, which includes the feasibility study, risk management, financing methods, in addition to expenditure mechanisms. The plan also covers the development of performance indicators, quality criteria, and manpower map required for production. Through this plan, the implementation process of the tasks assigned to different departments at each stage will be followed up and reported to ensure that GASTAT meets its clients’ requirements.
Appendix A: Q1 - 2023 Questionnaire Flow Charts
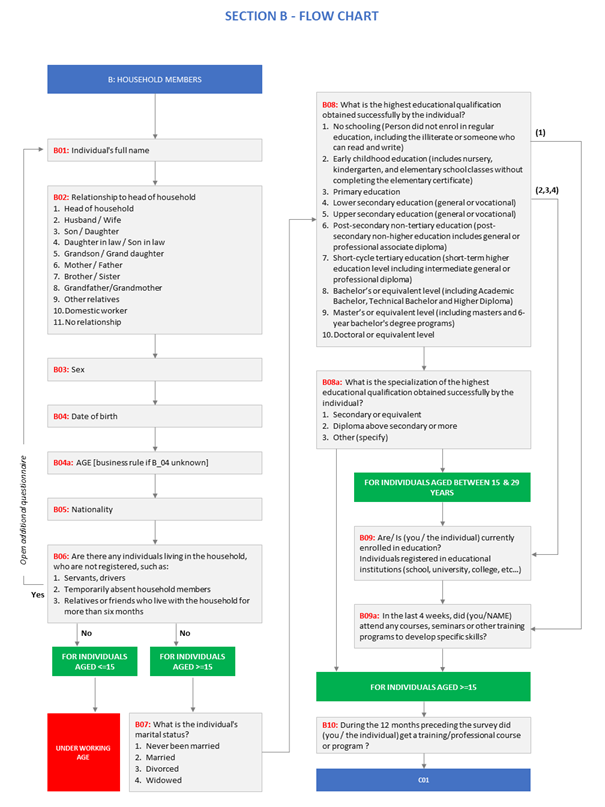

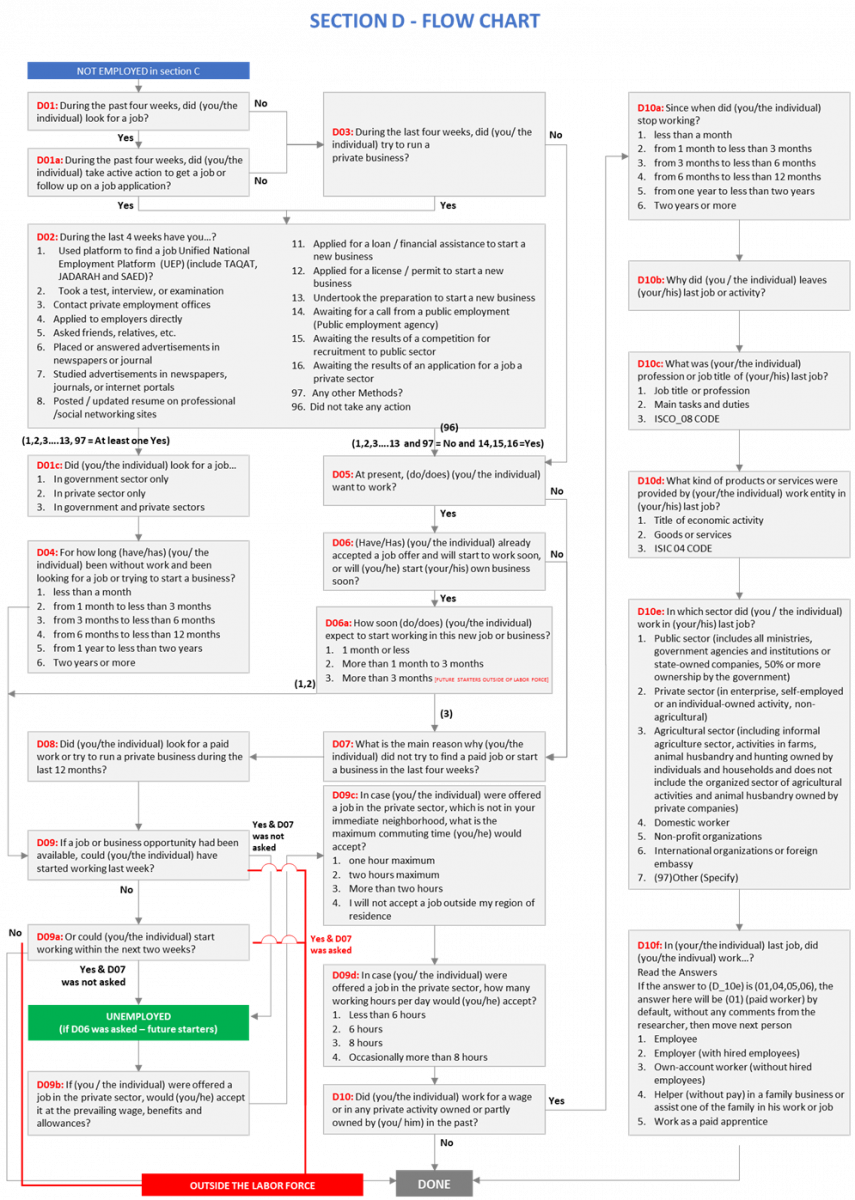
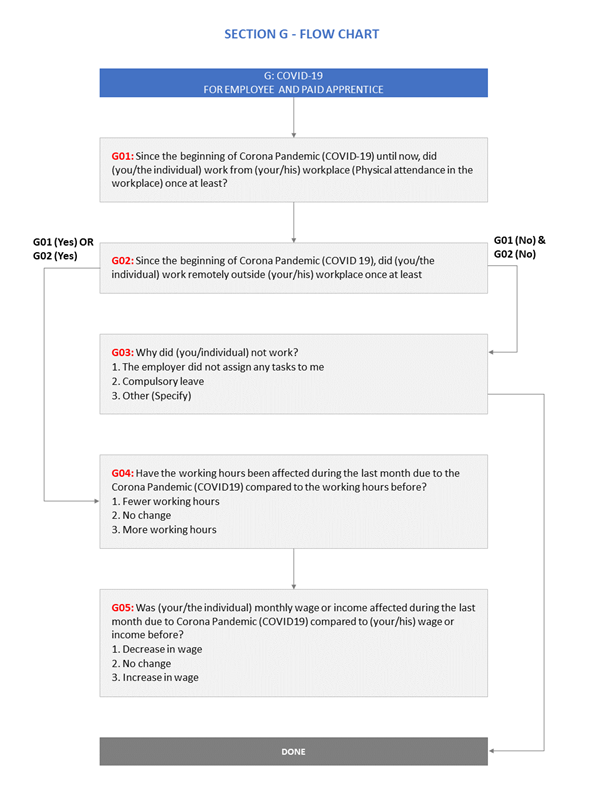
methodologies Series |
||
| Releases | links | |
| Fourth Quarter 2023 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| Third Quarter 2022 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| Second Quarter 2023 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| First Quarter 2023 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| Fourth Quarter 2022 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| Third Quarter 2022 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| Second Quarter 2022 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| First Quarter 2022 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| Fourth Quarter 2021 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| Third Quarter 2021 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| Second Quarter 2021 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| First Quarter 2021 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| Fourth Quarter 2020 | download survey form | |
| Third Quarter 2020 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| Second Quarter 2020 | download Methodology | download survey form |
| First Quarter 2020 | download Methodology | download survey form |
