Introduction
1. First: Scope
2. Second: Design
3. Third: Organization
4. Fourth: Data collection
5. Fifth: Disaggregation of data
6. Sixth: Revision
7. Seventh: Publication
8. Eighth: Evaluation
9. Ninth: Management
Introduction:
In all its statistical work, GASTAT applies a unified methodology suitable for the nature of each statistical product using the Statistical Procedures Guide approved by international organizations. Statistical products undergo 8 main phases, in addition to a ninth comprehensive phase, “Management”, as shown in the following diagram and
explanation underneath:
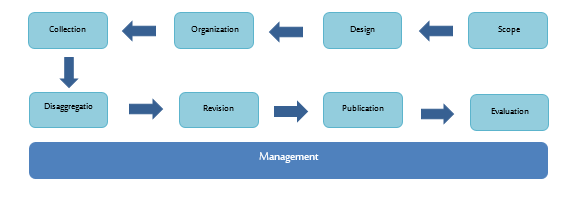
The first 3 phases (Scope, Design and Organization) are a cooperative process between GASTAT and its clients, represented by developmental entities data users, while Phase 4 (Data Collection) is done through GASTAT’s cooperation with the statistical population, whether families, businesses or holdings, in order to complete data and information. The remaining phases are statistical stages in which data is classified, reviewed and published. Then, Phase 8 (Evaluation) is carried out with clients. The Management Phase it is an administrative and organizational procedure applied across all phases. These phases have been applied to national account indicators as follows:
First stage: Scope:
The starting point of the preparation of the (National Accounts Indicators) and the first shared phase between GASTAT and other stakeholders from relevant entities, as well as the concerned departments inside GASTAT, such as: industry and business, external trade, and prices statistics department, in addition to government entities like: Ministry of Finance, SAMA, Ministry of Energy, Industry and Mineral. In this stage, GASTAT held workshops and meetings with entities to understand their needs and learn their requirements as the main data users. Their feedback was taken into consideration to ensure the realization of all the objectives of the Bulletin of National Account Indicators, which are:
- Provide estimates on GDP with (current and fixed) prices of the fiscal year, which show the expenditure on the GDP and measure the contribution of the economic activities and the different regulatory sectors.
- Provide the latest economic indicators as growth rates of GDP, as well as the relative contributions of economic activities and the different regulatory sectors of GDP.
- Provide statistics on national accounts based on the latest international systems.
- Provide a number of analytical tables that show the national economy paths as growth rates of GDP and its components as well as the shared cooperation between the main economic sectors.
In this stage, it was also ensured that the published statistics will contribute to fulfilling Vision 2030 as well as cover regional requirements, such as: GCC- STAT, Arab Monetary Fund, and the Arab League, in addition to international requirements represented in: Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia ESCWA, World Bank, and International Monetary Fund.
Second stage: Design:
Designing the statistical work as a comprehensive product by identifying the statistical population, designing the statistical framework, survey sample and form, as well as selecting data collection methods and tools and sampling units. Clients are involved in all of these procedures and their insights are taken into consideration in order to fulfill all their needs and include them in the final statistical product.
This phase’s main outputs are:
1.2. Statistics sources:
National Accounts indicators relay on administrative records available at relevant government entities as data source. These data are provided to GASTAT on a quarterly basis, to be calculated and released within the National Account Indicators’ Bulletin by GASTAT.
Administrative records include data and information registered at the relevant government entities that are concerned with national accounts.
2.2. Identifying the required data from the administrative records and determining methods of estimation:
In this step, data sources and some estimation methods were identified as following:
(a) Estimates at the current prices:
Below show the used methods for the economic activities to estimate the values of production, intermediate consumption, value added, and capital formation elements.
Agriculture and fishing:
Agricultural activity includes plant and animal production, fishing, forestry, logging, honey production, etc. The quarterly financial reports and financial statements of the major agricultural companies are the main source of activity data.
Crude petroleum and natural gas:
Estimations are conducted according to the information received to GASTAT from the petroleum companies working in KSA, through the Ministry of Energy, Industry and Mineral Resources
Mining and quarrying:
The estimation of the value of production and other elements such as intermediate consumption, value added , is through reports and financial statements of the companies of this activity.
Manufacturing:
Manufacturing covers the following subactivities:
- Manufacture of food products and soft drinks
- Manufacture of textiles, garments and leather
- Manufacture of wood and wood products including furniture
- Manufacture of paper, paper products, printing and publishing
- Manufacture of chemicals, chemical products, petroleum, coal, rubber, and plastic products
- Manufacture of non-metallic mineralsexcept petroleum and coal products
- Manufacture of basic metals
- Manufacture of metal products, machinery and equipment
- Other manufacturing
A sample of the quarterly financial reports and statements of major industrial companies is taken to estimate the added value of the activity.
Electricity, gas and water:
It includes activities of electricity, gas, steam, and air conditioning supply, in addition to sanitation and activities of wastes collection,, etc. reports and quarterly financial statements of Saudi Electricity Company are considered the main source of electricity data. On the other hand, private industry and gas companies are considered the main source of gas data. Finally, National Water Company is considered the main source of data of water production and distribution.
Value added is estimated according to method of production by using these data.
Building and construction:
This sector covers all building processes (of housing and non-housing buildings alike), as well as road construction and pavement, and construction of bridges, tunnels and railways, in addition to water, sewage, electricity, and telecommunication utilities. This sector covers, over and above, drilling wells, reclaiming land, installing airconditioning devices, connecting buildings to a water supply and sewerage network, as well as installing sanitary ware and elevators, aside from demolishing buildings, etc. The adopted estimation approach for this activity leverages a myriad of diversified methods. For example, national accounts variables are estimated according to the results of the economic researches and other sources such as annual final accounts and reports of data sources regarding the expenditure on new fixed assets by type of each asset.
Retail and wholesale trade, hotels and restaurants:
Includes wholesale and retail trade, repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles, as well as accommodation activities and food and beverage service activities. Estimates and calculations in this activity are based on the data provided by the quarterly financial reports and statements of the activity companies. It also provides data on procurement, sales, wages, commodity and service requirements and other income needed to estimate the value added of the activity
Transportation, communication, and storage:
This activity includes land transport, pipeline transportation, air and sea transport, warehousing activities, postal activities, parcel transportation, transportation support activities as well as communications activities whether the units are from public or private sector orboth. It also includes publishing, computer programming, consultancy, information service activities, programming, broadcasting, etc. The estimation of the value added of this activity is based on the data provided by the quarterly financial reports and statements of the major companies engaged in telecommunication, transport and storage activities
Finance, insurance, real estate and business services
It includes money and insurance services, financial services activities, insurance and reinsurance financing activities and pension funds, in addition to auxiliary activities for financial services and insurance activities. It also includes real estate activities such as residential rents plus business services activities, legal activities, accounting, research and development activities in the scientific field, advertising and market research activities, etc. Residential rents are estimated by using the available data of Household Expenditure and Income Survey (2013), taking into account the growth rates of population. As for business services, they depend on the quarterly financial reports and statements of major companies of the activity.
Personal, social, and community services:
It includes education services, human health activities, care with accommodation and group work without accommodation services. It also includes all arts, amusement, and creativity activities as well as sport, computer maintenance, home and personal activities, etc.
Reports and financial statements are the main source of data.
Government services:
Public governmental sector provide goods or services for free or at nominal prices. There is no market value for the production of governmental services; therefore, the production is estimated through expenditure. In other words, total production is equal to total input requirements, plus the compensation of workers and depreciation, and by subtracting the input requirements from the value of production (method of production) you get the total benefit, which is equivalent to the compensation of workers plus depreciation, therefore, there is no net surplus for the government sector.
Data received from Ministry of Finance on revenues and quarterly expenses are the only source to estimate the value added of governmental services.
(b) Estimates at constant prices:
(2010) is the used base year to prepare national accounts at fixed prices. The different stabilization methods for each economic activity varied according to the available information. Below are the methods followed to make the estimates at fixed prices:
Agriculture, forestry, and fishing:
The index of production quantities, whether plant, animal or fish, was used to find the output value at constant prices.
Crude oil and natural gas:
Due to the availability of quantities produced in barrels, estimates were based on the index of those quantities.
Oil refining:
Depending on the availability of product quantities from the refining process, a quantitative index has been composed to prepare estimates at constant prices
Other manufacturing industries:
The wholesale price index is used to prepare the estimates in current prices
Electricity, gas, and water:
Estimates were calculated based on the sold quantities.
Construction:
Wholesale price index of construction materials was used to prepare the estimates.
Wholesale and retail trade, restaurants, and hotels:
General index of wholesale and retail trade, restaurants, and hotels was used to prepare the estimates.
Transportation, storage, information and telecommunication:
Transportation and telecommunication price index was used to prepare the estimates.
Banking services:
Implicit GDP index is used in re-evaluating the estimates in current prices to estimates in constant prices.
Rents (buildings):
The cost of living index of rents was used to find the estimates at constant prices.
Personal, social, and community services:
Cost of living index was used to re-evaluate the numbers at current prices to the number at constant prices.
Seasonal adjustments:
Seasonal adjustment is carried out with (TRAMO-SEATS) method based on ARIMA (Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average) model of estimation suggested by International Organizations.
3.2. Concepts and terms of National Accounts Bulletin:
Gross Output:
The value of Goods and services resulted from producing activity for institutional units that use input during the accounting period. It includes finished, unfinished and the products produced for own use. The value of output is usually estimated at producer prices, that represents the market value at factory gate.
Intermediate Consumption:
It is the value of goods and services that is used as inputs for the production process excluding fixed assets as their consumption is considered as a consumption of the fixed capital. The used goods and services might be totally transformed or consumed in the production process. Some inputs may emerge again after being transformed or merged with the outputs. There are some inputs that can be totally disappeared such as electricity and other similar services.
Gross Domestic Product (by production approach):
The total value added of the resident producers at producer price,in which customs fees or output totals are added and the total intermidate consumption are deducted and the net products taxes are added (taxes- subsidies ),which are not included in the outputs value.
Gross Domestic Product (by expenditure approach):
The total of final expenditure at purchasers’ price including exports at free on board prices (FOB), from which imports are deducted.
Indirect taxes:
The term refers to the taxes imposed on producers for producing, selling, buying, or using goods and services. Indirect taxes are usually added to production costs, and include customs fees.
Production Subsidies:
Subsidies are the government payments awarded to the producers of the public and private sectors. It also includes the public authorities payment for government projects to compensate any loss that results from any government policy to keep the price at a fixed level. The subsidies might also be calculated as the difference between the targeted price and the actual market price paid by the purchaser. This difference must be compensated by government.
Net indirect taxes:
They are the value of indirect taxes minus the value of production subsidies.
Depreciation of Fixed Capital:
It represents the decrease of the fixed assets value, used in production, during the accounting period as a result of a slump, obsolescence, or any deterioration factor. This depreciation could be deducted from the fixed capital formation to get the net fixed capital formation
Financial intermediation services indirectly measured (banks):
It is the difference between interest value and profits payable to banks and financial institutions on the one hand, and the value of interests payable to depositors on the other hand
Seasonally Adjusted Gross Domestic Product:
It is the process of removing the effects of seasonal fluctuations such as climatic conditions, public holidays and change in holidays days from Quarterly Gross Domestic Product by Economic activities at 2010 constant prices data.
Imports of :Goods and Services:
It is the value of goods that have been transferred from being owned by non- residents to being owned by residents in Saudi Arabia. Moreover, the imports include the services provided by nonresidents to residents in Saudi Arabia. The imports include, the goods that cross the boards for processing. and the goods that prepared in foreign ports and transported by local transporters, nonmonetary gold. The import services include tourism and transportation services, communication, insurance, construction, financial services, royalties, licenses fees, personal and cultural services, and non-classified government services.
Exports of Goods and Services:
It is the value of goods that have been transferred from being owned by residents in Saudi Arabia to being owned by non-residents. The exports include exported goods for processing, goods purchased in local ports by non-residents transporters, and nonmonetary gold. However, the exports of services include all services provided to non-residents such as tourism and transportation services, communication, insurance, financial services, royalties, licenses fees, personal, cultural, and recreation services, and government services.
Government Final Consumption Expenditure:
The value of the total goods and services that consumed by the government in the process of producing the government services. It equals the value of the government total production minus the value of the market and non- market sales. The government production value equals the intermediate consumption of goods and services in addition to the value of the compensation of employees, depreciation of fixed capital, and indirect taxes.
Households Final Consumption Expenditure:
The value of resident households final consumption expenditure on goods (durable and non-durable) and services minus their sales of used goods.
Final Consumption Expenditure of NPISHs:
The value of the NPISHs final consumption expenditure on goods and services that are provided free or at nominal price to households. This equals the value of production minus market and non- market sales.
Private Final Consumption Expenditure:
The value of final consumption expenditures of resident households and the NPISHs.
Gross Fixed Capital Formation:
The values of the net addition of the producers to the fixed assets minus the value of fixed assets disposed of by producers (additions - exclusions) (additions – eliminations) during the accounting period. In addition to additions made to non-productive assets such as land improvement, forest development, implantations and groves …etc. These additions are used for more than one year. They include changes in live-stock such as dairy livestock …etc. They also include transferring (sales and purchases) property costs regarding lands, forests, and mines …etc.
Change in Stock:
The market value of change that occurs during the accounting period of stock including raw material, product in process, finished products, animals for slaughtering, and purchased goods for resale. This represents the difference in the stock value at the end and at the beginning of the accounting period.
Gross Capital Formation:
It equals the value of fixed capital formation in addition to the change in stock.
4.2. Used statistical classifications:
Classification is identified as an organized group of related categories which are used to collect data according to similarity. Classification is the base for data collection and dissemination in various statistical fields, such as: (economic activity, products, expenses, occupations or health…. etc). classifying data and information helps to put them in meaningful categories to produce useful statistics. In fact, data collection requires an accurate organization and based on their common features to create reliable and comparable statistics. On the other hand , National Account Indicators are based on the international standards of data collection and classification and rely on the following classifications :
1. The National Classification of Economic Activities (ISIC 4):
It is a statistical classification based on ISIC4 which is the reference of the productive activities. This classification was used in the Labour Force Survey to identify the main economic activities of the establishment where an individual works. Economic activity can be defined as (all the practiced activities or works and services provided by the establishment that make a financial return, sometimes the establishment does not gain any financial return from its works as in charity institutions that rely on donations ).
2. Central Product Classification (CPC2):
CPC forms a complete classification for products including goods and services. Purpose of this classification is to create an international standard for collecting and categorizing all types of data that require some details of the product, including the industrial production, national accounts, services industries, internal and external trade of major goods, international trade in services, payments balance, consumption, prices statistics. In addition to other main purposes such as: provide an international comparable framework, activate the coordination between various types of statistics related to goods and services.
3. Classification of individual consumption by purpose (COIPCOP):
It is used to define individual’s expenditure as well as individual’s consumption
4. Classification of the Function of Government (COFOG):
The classification of the function of government in line with the UN System of National Accounts (SNA in collaboration with the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development OECD is one of the pillars of the manual.It classifies 'government expenditures' by their functional nature to measure the extent to which government expenditures meet their overall objectives, helping analysts and government performance monitors assess the effectiveness of government spending.
5. Balance of Payments Manual as per the Sixth Edition:
The Balance of Payments Manual (sixth edition), which is prepared by the International Monetary Fund, is one of the most important statistical systems that is used within the National Accounts System 2008. The accounts of the outside world sector within the National Accounts System is considered the linking point between the two systems. The two systems are similar in that they both include the same recommendations either to view accounts or to record and evaluate transactions .
Third stage: Organization:
It is the last stage of the preparation that precedes data collection. In this stage, the work procedures required for preparing the bulletin was completed; which will start from the following stage “data collection” and will end in the “evaluation stage”, organizing and collecting those procedures, identifying the appropriate sequence for them in order to come up with a methodology that meet the objectives of national account indicators. At this stage, the procedures that were done in the preparation of the previous version of the bulletin were reviewed to develop the work procedures in this version. These procedures were also described and documented to facilitate the updates of the future releases. Furthermore, the statistical work procedures were examined and tested to ensure that they meet the requirements of the preparation of the national account indicators in its final form . On other hand, the statistical work procedures as well as the execution road map were all approved.
Fourth stage: Data collection:
GASTAT has coordinated with the concerned government entities and establishments to obtain the data of national account indicators based on the administrative records available at those entities. Data were also stored in GASTAT database, revised according to the scientific statistical methodology as well as the recognized quality criteria in coordination with the data source.
Fifth stage: Disaggregation of data:
Raw data of National Account Bulletin were disaggregated according to the classification and coding inputs that were completed in data collection stage. In fact, data were disaggregated based on ISIC4 , CPC2, COFOG, COICOP, in addition to the Balance of Payment Manual (6 edition). Data of national account bulletin were presented in appropriate tables to facilitate the process of summarization, comprehension, results extraction, and comparison with other data. In other words, it is easier to refer to them when they are presented in clear tables.
In this stage, data were processed according to the following steps:
First: data logicality and comprehensiveness:
Data were revised in an appropriate way to ensure their comprehensiveness, logicality, and accuracy for more accurate statistics. Therefore, data of the current release are compared with the data of other releases to validate its logicality, extract, and revise the results in the following stages.
Second: data confidentiality:
Data are kept confidential at GASTAT and are only used for statistical purposes. What is prepared for publishing are only aggregated statistical tables for a number of national account variables.
Sixth stage: Revision:
First: data outputs validation:
After revising the register-based data in the fourth stage to check their accuracy, GASTAT worked on calculating and extracting the results, downloading the outputs and storing them in the database. Specialists of national account statistics department conducted the final revision by using the latest technologies and software that were designed for revision and editing purposes.
Second: dealing with confidential data:
According to the Royal Decree No. 23 dated 07-12-1397, data shall be kept confidential, and shall be used by GASTAT only for statistical purposes. Therefore, data are stored in GASTAT’s data servers.
Seventh: Publication:
First: preparing and processing the results designed for publishing:
In this stage, GASTAT coordinated and organized the data of the administrative records included in the bulletin. After that, publishing tables and charts of data and indicators were all prepared, methodology and metadata were added to them as well. Data are available in English and Arabic.
Second: preparing media kit and announcing the date of the release:
GASTAT has already announced the bulletin’s release date at the beginning of the calendar year on its official website. In this stage, GASTAT worked on preparing the media kit to announce its release on different media platforms. However, the bulletin will be published first on GASTAT official website in open formatting (Excel), which will facilitate the access by all clients and those who are interested in national account statistics. The bulletin will also be uploaded to the statistical library on GASTAT’s website.
Third: Communicating with clients and providing them with the bulletin’s results:
Due to the importance of communication with clients, GASTAT always provide them with the bulletin right after its publishing on the website. It also receives the clients’ questions and inquires about the bulletin and its results through different communication channels, such as:
- GASTAT’s official website www.stats.gov.sa
- GASTAT’s official e-mail address info@stats.gov.sa
- Client Support’s e-mail address cs@stats.gov.sa
- Official visits to GASTAT’s head office in Riyadh or one of its branches in Saudi Arabia.
- Official letters.
- Statistical helpline (920020081)
Fourth: Preservation of thePublished Content:
To ensure that the contents of the publication are preserved for long periods of time, the documents and archives center in the Authority preserves and archives the published data to be used as a reference at any time whether for the Authority or for others if necessary.
Eighth stage: Evaluation:
In this stage, the statistical work procedures will be evaluated for further improvement in order to get high quality data. The improvement includes methodologies, procedures, systems, statistical researchers’ skills, and the statistical framework. This stage is completed in partnership with data users as well as GASTAT clients through a number of steps:
First:Collection of Measurable Evaluation Inputs:
In this step, the most important comments and notes are collected and documented from their sources in different stages, for example comments and notes given by data collectors and their field supervisors as well as data providers. Also, notes written by specialists responsible for reviewing, auditing and analyzing data collected either from field or administrative records. Finally, comments and notes collected and documented by data users after publishing the data .
Second: evaluation:
The evaluation is completed by analyzing the collected inputs and by comparing the results of the analysis with the previously expected results. Based on that, a number of possible improvements and solutions are identified and discussed with the concerned entities . During this step, clients' performances and satisfaction levels of using National Account Bulletin results are measured.
Ninth stage: Management:
It is a comprehensive stage required to carry out each phase of national account bulletin production. During this stage, the plan of production is developed, which includes the feasibility study, risk management, financing methods, in addition to expenditure mechanisms. The plan also covers the development of performance indicators, quality criteria, and manpower map required for production. Through this plan, the implementation process of the tasks assigned to different departments at eachstage will be reported to ensure that GASTAT meets its clients’ requirements .
