-
Overview
-
Agriculture Census Importance
-
Historical Background
-
Time reference
-
Agricultural Census Inclusiveness
-
Phases of the agricultural census implementation
-
Agricultural Census Methodology
-
Glossary
Overview:
Agriculture is acknowledged to be of great significance for humans and animals alike. It provides them with the most essential strategic stocks of indispensable staple food in all circumstances. Grains and feed are necessary for livestock that provide humans with meat and milk. Besides, vegetables, fruits and dates are reckoned important for food security. As a matter of fact, some agricultural products supply raw materials needed for the production of many necessary food products.
Accurate and comprehensive statistical data on all agricultural holdings should be supplied. To that end, GAStat seeks to provide such data by carrying out a comprehensive census aiming at supplying as many statistical tables containing the most important data and statistical indicators as needed for planning and developing agricultural strategies. The agriculture census is the key source of agricultural information as it covers all agricultural holdings in KSA. Moreover, it demonstrates data on characteristics of all agricultural holdings characteristics at all geographic and administrative levels in KSA. It also presents an integrated, up-to-date framework for future agricultural surveys based on sampling.
Agriculture Census Importance:
Importance and objectives of the agriculture census are as follows:
- To update the current agricultural holdings framework by administrative divisions in KSA;
- To get detailed data on agricultural holders and their social characteristics;
- To get detailed data on the labor force by labor category, gender and nationality, in addition to obtaining detailed data about permanent labor by the education level;
- To acquire detailed data on the structure of agricultural holdings in terms of the following variables:
- Total cultivated areas
- Utilizations of these areas by the agriculture type and the production specialization
- System and sources of the irrigation and the used energy
- Crop structure (permanent, winter and summer)
- Data on the protected agriculture of vegetables and cut flowers
- Numbers and types of fruiting and non-fruiting palm trees
- Numbers and types of fruitful and fruitless permanent trees, except palm trees
- Number of livestock included in traditional and specialized holding
- Number of birds and poultry in traditional and specialized holding
- Data on fish aquaculture farms
- Data on the number of hives in holdings
- Number of the used agricultural machines;
- Data on buildings and constructions by type, number and area of lands or floor area ratios of these buildings and constructions
- Data on agricultural extension sources
- Data on funding sources in agricultural holdings
- To create an integral relation between the agricultural census and the specialized statistical surveys, implemented periodically by way of statistical sampling, with the aim of ensuring inclusiveness in monitoring all achievements in various sub-activities covered by plant and animal agricultural activity;
- To provide researchers, students and whoever interested in the agricultural activity statistical data to be used in research and studies that contribute to highlighting and developing agricultural activity in the Kingdom; and
- To conduct local, regional and international comparisons for the agricultural sector.
Historical Background
The Ministry of Agriculture carried out the first agricultural census in 1973 -1974, the second in1982, and the third in 1999.
Afterwards, GAStat implemented the fourth census in 2015, which is its first agricultural census.
Time reference:
The time reference of data on holding, holders, agricultural labor, agricultural crops, machinery and equipment and agricultural applications is the agricultural year which begins from March 2014 till February 2015.
As for the time reference for livestock data, it is the day in which animals and poultry of all types are enumerated. This day is February 1st, 2015, corresponding to Dhul-Hijjah 4th, 1436 H.
Agricultural Census Inclusiveness:
The agricultural census involves:
- All farmland included in agricultural holdings outside in the approved administrative organization of cities and villages by organizational schemes provided by municipalities
- Old holdings included in the administrative organization of cities and villages
- Agricultural holdings in which livestock are bred stably, and which contain at least one camel, one cow, fifteen heads of sheep or goats, thirty chicken or five bee hives.
- Fish Aquaculture farms
- Poultry farms of various types
The Agricultural census does not include:
- Economic units engaged in activities not listed in the scope of the agricultural census, namely:
- Fishing, hunting and breeding wild hunting animals,
- Forestry or logging,
- Parks and public gardens,
- Private and government nurseries,
- Agricultural Services establishments,
- Marine fisheries,
- Private bunkhouses which are not designed to direct agricultural economic exploitation, and
- Cattle sale yards.
Phases of the agricultural census implementation:
First: The phase of numbering and counting the agricultural holdings and the stockbreeders not included in such holdings:
A) Numbering and counting agricultural holdings:
This phase provided a framework for agricultural holdings across KSA to be used in the agricultural census and future agricultural surveys carried out through sampling at the level of all administrative divisions (administrative region, province, municipality, locality).
This phase provided also data on the geographical distribution, in addition to data on coordinates of all agricultural holdings in KSA.
B) Counting stockbreeders outside holdings (holdings without land):
Counting stockbreeders outside holdings is carried out simultaneously with the phase of numbering and counting agricultural holdings. Based on this process, an estimate of the number of stockbreeders who are outside the holdings and within the municipality are provided with the aim of fulfilling detailed data about them in the counting phase.
Second: The Phase of Actual Counting:
Census methodology requires the statistical researcher to visit each holding counted during the phase of numbering and counting. Actually, the data of traditional and specialized farms are electronically collected whereas the data of stockbreeders existed in the outskirts of villages and the desert are collected on papers to be recorded on computers after that.
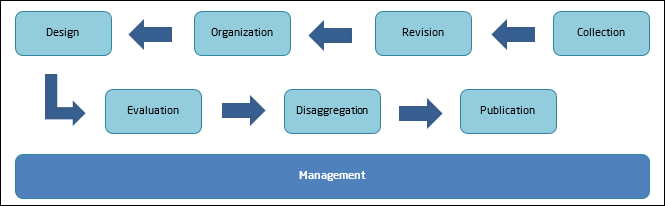
Agricultural Census Methodology:
- Adopting the method of actual measurement of the cultivated area of various crops, the greenhouses areas, warehouses, barns, poultry hangers, fish aquaculture basins and the like;
- Adopting the method of actual counting of palm trees, fruit trees, animals, operational machinery and equipment owned by the holder and others;
- Ensuring data that cannot be obtained by measurement or counting, through asking the holder or his representative;
- Using an electronic form downloaded on tablets for the field data collection along with downloading self-correction controls so that any error or inconsistency in the data is immediately corrected before leaving the holding;
- Using a paper form to fill up the data of the stockbreeders in the desert.
Glossary
Holding:
It refers to an economic unit of the agricultural production of crops and livestock. Coming under one management, the holding covers all animals included in it and all lands used fully or in-part for agricultural production, regardless of the ownership, the legal form or the area. The holding may be managed by one individual or a family and may also be managed by two or more individuals or families jointly. This management may be undertaken by a corporate body such as a company, a cooperative, a government agency or others. The holding land may consist of one or more parts included in one locality provided that all parts of the holding use the same production means; e.g., labor or agricultural machinery and equipment, evidently and distinctly to the extent that these parts are considered one economic unit.
Holder:
Holder is an individual or legal person (company or governmental body) exercises management control over the agricultural holding and investment. Furthermore, he takes the main decisions related to the use of available resources. He is also technically and economically responsible for the holding and has the right to assume all responsibilities directly or to delegate management responsibilities to a paid manager. If two or more family members manage the same holding, the family head will be the holder.
Owner:
He is an individual or legal person (institutions, companies or government agencies) to whom the holding land ownership is assigned by virtue of a title deed (a legal instrument, a common instrument, a distribution decision, a farming lease, etc.) The owner may be the holder himself.
Total Area of the Holding:
It is the area of all parts of the holding put together, including the owned area or the area rented from others and any areas held by the holder in accordance with other exploitation rights. The total area of the holding excludes the holder's area if it is rented to other. The holding consists of cultivated lands and lands occupied with a farmhouse, animal shelters, yards and roads. Dunam is used as a measurement unit to measure the holding area. One dunam is equivalent to 1,000 square meters.
Holder's Legal Entity:
The legal entity of the holder takes one of the following forms:
individual, institution, corporation, partnership, a government body, a cooperative, or other.
Land Holding System:
This term refers to arrangements or rights under which the holder is able to hold and use the land.The land holding system in one of the following labels: owned, leased, owned and leased, or others.
Holding Management Method:
It means the person involved in managing agricultural holding activities, using its components and monitoring the implementation of these actions. The person concerned in the holding management might be the holder, a paid manager, a family member, or other.
Main Purpose of Production:
The main purpose of production might be: sale or consumption.
Holding Type:
The holding type takes one of the following forms: traditional or specialized.
Holding Main Activity:
It is the prevailing activity practiced by the holding and is consistent with its economic revenues; such that represents more than 50% of the annual income of that holding. For the purposes of the agricultural census, the holding main activity has been divided into five sections, namely: (Plant, animal, poultry, fish, or mixed).
Holder's Main Job:
It is the main work exercised by the holder during the most of the usual work hours. It is one of the following occupations: (agriculture or non-agriculture).
Agricultural Worker:
He is an individual who worked in the holding for some time during the agricultural year of the census, whether he was paid in cash or in kind. It should be noted that if an individual worked several times in the holding in the course of the agricultural year, it will be considered as one time along with aggregating his work periods will be aggregated to be one period. Agricultural workers are classified into three main
categories as follows:
- Permanent Agricultural Worker: A person who works regularly and continuously in the holding during the agricultural year; besides, he usually spends more than six months in the holding. Actually, the holder is one of the permanent labor if his main occupation is "agriculture".
- Temporary agricultural worker: An individual who works irregularly and inconstantly in the holding during the agricultural year. Temporary workers are mostly employed for short periods ranging between three and six months to accomplish limited tasks, such as picking fruits. Their services are terminated along with completing the task entrusted to them.
- Casual \ Occasional Agricultural Worker: An individual who works irregularly and impermanently in the holding during the agricultural year. Casual \ occasional workers are mostly employed for short periods (less than three months) to carry out limited tasks, such as picking fruits. Their work tenure are terminated on completion of the the tasks assigned to them.
Irrigation Water Sources:
The following main sources used to irrigate the holding:
(Artesian aquifers, Hand-dug wells, Wellsprings, Dams, Springs, Rains, Other sources of irrigation).
Energy Sources Used for Irrigation:
They are the key sources used by the holding for irrigation.The energy sources are divided into:
(Public electricity, Private electricity, Petroleum products, or Other; the holding does not have any energy source).
Petroleum Products Used in the Holding:
They include all petroleum products, such as diesel, gasoline and oils, used in the holding during the census year, whether for irrigation or to run engines, machinery, generators, automated equipment and transportations allocated for the holding activities.
Agricultural Season:
The agricultural season is divided into two main types, namely: (Winter Season and Summer Season).
Crops Cultivation:
It is the way or method adopted to plant crops. The crops cultivation is divided into three main ways: (Single crop, Inter-crops and called also paired crops, Successive crops).
Holding Irrigation Method:
The holding is irrigated in one of the following ways:
- Flooding Irrigation: It is the traditional method applied on irrigating the holding cultivated lands, which are watered through surface earthen canals distributing water for crops.
- Modern Irrigation: It is the method applied on irrigating the holding cultivated lands through a modern irrigation system such as drip irrigation, pivot or stationary sprinkler irrigation, gun sprinkler irrigation or any other modern irrigation method. In most cases, this technique is used in large,specialized and modern holdings that have special irrigation systems. Some of prominent modern irrigation methods are:
- Drip irrigation
- Sprinkler irrigation
- Rain Irrigation This method relies on rain to water the holding cultivated lands. This system is widely used in the south of KSA in general.
Specialized Cattle Farms:
They are holdings concerned with breeding cattle for commercial purposes. They contain stalls, stockyards for breeding, an automatic chilled milking room or a chilled warehouse and a fodder storeroom, etc.
Poultry and Birds in Unspecialized Holdings:
They cover all poultry in holdings unspecialized in the production of poultry such as chickens and pigeons ... etc.
Specialized Poultry Farms:
Specialized poultry farms are divided into the following:
- Broiler chicken farms
- Laying hens farms
- Broiler Chicken parents farms
- Laying hens grandparents farms
- Broiler chicken grandparents farms.
- Laying hens parents farms.
- Other farms: They are poultry farms specialized in other types of poultry except chicken, such as the farms of ostrich and quail ... etc.
Fish Aquaculture farms:
They are small lakes or ponds of fresh water or salt water designated for fish farming in the holding for the purpose of breeding or fish production.
Beehives (in Holdings):
Beehives are divided into: Normal (traditional) cells or artificial (modern) cells
Agricultural Machinery and Equipment:
They cover various agricultural machinery, automated equipment, water pumps, tractors, harvesters, seeding machines, sprayer pumps and other machines owned by the holder or rented from others. These machines may be used for agricultural and animal production wholly or partially. The machinery and equipment shall not include the machinery used for any purposes other than agriculture during the agricultural year of the census.
Fertilizers:
They are chemical, natural, organic or manufactured materials added to soil or irrigation water according to specific rations to provide plants with the necessary nutrients, which contain at least 5% of one or more of the three nutrients (nitrogen, phosphate, potassium).
Pesticides:
They involve concentrated manufactured chemicals to be diluted before usage through adding different materials such as water, kerosene, etc. to them. They are used to mitigate the impact of harmful pests on crops or animals, and to eliminate them.
Agricultural Extension :
It is an educational informal process designed to serve and educate farmers and their families, to make use of their available potentials and their own efforts, to help them improve their social and economic levelthrough using modern scientific methods and techniques in the development of farmers' skills; consequently, the agricultural production is promoted and increased. The agricultural extension sources are as follows:
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Cooperatives
- Agricultural materials sale companies / shops
- Other farmers
- The media
- Other sources of extension, such as Agricultural Development Fund, Colleges of agriculture and Agricultural Fairs, etc.
Funding Sources:
This expression refers to the entities resorted to by the holder to get funds to finance the holding private, provided that these funds are used to finance agricultural projects inside the holding, not the outside projects or any other non-agricultural activities. The sources of funding are:
(Agricultural Development Fund, Commercial Banks, Individuals, the Holder, or Other Sources of Funding).
